Relative efficacy of T cell stimuli as inducers of productive HIV-1 replication in latently infected CD4 lymphocytes from patients on suppressive cART
- PMID: 28527342
- PMCID: PMC5654527
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2017.05.008
Relative efficacy of T cell stimuli as inducers of productive HIV-1 replication in latently infected CD4 lymphocytes from patients on suppressive cART
Abstract
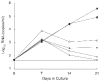
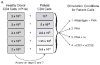
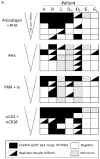
Quantification of cell-associated replication-competent HIV, in blood samples from patients with undetectable plasma viremia, requires specialized culture conditions that include exogenous pan T cell stimulation. Different research groups have used several stimuli for this purpose; however, the relative efficacies of these T cell stimuli to induce productive HIV replication from latently infected cells ex vivo have not been systematically evaluated. To this end, we compared four commonly used T cell stimuli: 1) irradiated allogeneic cells plus phytohaemagglutinin (PHA); 2) PHA alone; 3) phorbol myristate acetate plus Ionomycin; and 4) immobilized αCD3 plus αCD28 antibodies. End-point dilutions of patient CD4 T cells were performed, using virion RNA production to quantify HIV induction. Our results demonstrated that these activation approaches were not equivalent and that antibody cross-linking of CD3 and CD28 membrane receptors was the most effective means to activate HIV replication from a resting cell state, closely followed by stimulation with irradiated allogeneic cells plus PHA.
Keywords: Assay optimization; Cell-associated infectious units; HIV latency; T cell stimuli.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Archin NM, Bateson R, Tripathy MK, Crooks AM, Yang K-H, Dahl NP, Kearney MF, Anderson EM, Coffin JM, Strain MC, Richman DD, Robertson KR, Kashuba AD, Bosch RJ, Hazuda DJ, Kuruc JD, Eron JJ, Margolis DM. HIV-1 expression within resting CD4+ T cells after multiple doses of vorinostat. J Infect Dis. 2014;210:728–735. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Archin NM, Liberty AL, Kashuba AD, Choudhary SK, Kuruc JD, Crooks AM, Parker DC, Anderson EM, Kearney MF, Strain MC, Richman DD, Hudgens MG, Bosch RJ, Coffin JM, Eron JJ, Hazuda DJ, Margolis DM. Administration of vorinostat disrupts HIV-1 latency in patients on antiretroviral therapy. Nature. 2012;487:482–485. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

