Induction Effect to Apoptosis by Maitake Polysaccharide: Synergistic Effect of Its Combination With Vitamin C in Neuroglioma Cell
- PMID: 28528571
- PMCID: PMC5871285
- DOI: 10.1177/2156587217708524
Induction Effect to Apoptosis by Maitake Polysaccharide: Synergistic Effect of Its Combination With Vitamin C in Neuroglioma Cell
Abstract
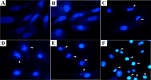
Polysaccharide extracted from the Maitake mushroom (MP) is considered as a potential anticancer agent. The present study was performed to investigate the cytotoxic effects of MP and vitamin C (VC) alone and in combination on the viability of human neuroglioma M059 K cells in vitro. A combination of MP (1.0 mg/mL) and VC (0.4 mmol/L) led to a 53.10% reduction in cell viability and this treatment induced cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase, and apoptosis occurred in 38.54% of the cells. Results of Hoechst 33258 staining and Western blot showed apoptotic cells appeared and changes in the expression of apoptosis-related proteins (upregulation of Bax and caspase-3, downregulation of Bcl-2, and activation of poly-(ADP-ribose)-polymerase). Moreover, the activities of caspase-3, caspase-8, and caspase-9 were enhanced in M059 K cells. The inhibiting effect of combined treatment with MP and VC on M059 K cells indicates the mechanism of anticancer activity involved induction of cell apoptosis.
Keywords: Maitake; antitumor; apoptosis; neuroglioma; vitamin C.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Omuro A, DeAngelis LM. Glioblastoma and other malignant gliomas: a clinical review. JAMA. 2013;310:1842–1850. - PubMed
-
- Johnson DR, Galanis E. Medical management of high-grade astrocytoma: current and merging therapies. Semin Oncol. 2014;41:511–522. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009; 10:459–466. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

