Transcriptional and Post-transcriptional Gene Regulation by Long Non-coding RNA
- PMID: 28529100
- PMCID: PMC5487525
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gpb.2016.12.005
Transcriptional and Post-transcriptional Gene Regulation by Long Non-coding RNA
Abstract
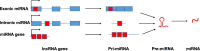
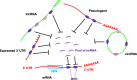
Advances in genomics technology over recent years have led to the surprising discovery that the genome is far more pervasively transcribed than was previously appreciated. Much of the newly-discovered transcriptome appears to represent long non-coding RNA (lncRNA), a heterogeneous group of largely uncharacterised transcripts. Understanding the biological function of these molecules represents a major challenge and in this review we discuss some of the progress made to date. One major theme of lncRNA biology seems to be the existence of a network of interactions with microRNA (miRNA) pathways. lncRNA has been shown to act as both a source and an inhibitory regulator of miRNA. At the transcriptional level, a model is emerging whereby lncRNA bridges DNA and protein by binding to chromatin and serving as a scaffold for modifying protein complexes. Such a mechanism can bridge promoters to enhancers or enhancer-like non-coding genes by regulating chromatin looping, as well as conferring specificity on histone modifying complexes by directing them to specific loci.
Keywords: Epigenetics; Long non-coding RNA; MicroRNA; Post-transcriptional regulation; Transcriptional regulation.
Copyright © 2017 Beijing Institute of Genomics, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Genetics Society of China. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Johnson J.M., Edwards S., Shoemaker D., Schadt E.E. Dark matter in the genome: evidence of widespread transcription detected by microarray tiling experiments. Trends Genet. 2005;21:93–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

