Induction of proteotoxic stress by the mycotoxin patulin
- PMID: 28529145
- PMCID: PMC5516271
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2017.05.015
Induction of proteotoxic stress by the mycotoxin patulin
Abstract
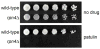
Patulin is a naturally occurring mycotoxin produced by a number of molds and may contaminate a wide variety of food products. In practice, patulin's main societal relevance concerns apple juice and its products. Multiple advisory bodies, including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the World Health Organization, recommend that producers monitor and limit patulin levels in apple juice products. The mechanism of patulin toxicity remains largely unknown. Here we show that patulin induces proteotoxic stress in the yeast S. cerevisiae. The transcription factor Rpn4 controls the abundance of the proteasome, the complex multisubunit protease that destroys proteins, including misfolded proteins. Rpn4 protein is strongly induced by patulin, and Rpn4 levels normalize over time, consistent with homeostatic regulation. A rpn4Δ mutant is highly sensitive to patulin, confirming the physiologic relevance of this response. Rpn4 is known to be regulated both transcriptionally and post-translationally. Patulin induces both pathways of regulation, but the post-transcriptional pathway predominates in controlling Rpn4 protein levels. These results indicate that proteotoxicity represents a major aspect of patulin toxicity. They not only have implications for patulin detoxification but in addition suggest the possibility of some potentially useful patulin applications.
Keywords: Patulin; Proteasome; Proteotoxicity; Rpn4; Yeast.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
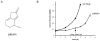

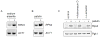


References
-
- Cox JS, Walter P. A novel mechanism for regulating activity of a transcription factor that controls the unfolded protein response. Cell. 1996;87:391–404. - PubMed
-
- Fliege R, Metzler M. The mycotoxin patulin induces intra- and intermolecular protein crosslinks in vitro involving cysteine, lysine, and histidine side chains, and alpha-amino groups. Chem Biol Interact. 1999;123:85–103. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

