Nitroalkane oxidase: Structure and mechanism
- PMID: 28529198
- PMCID: PMC5650508
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2017.05.012
Nitroalkane oxidase: Structure and mechanism
Abstract
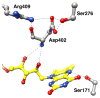
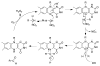
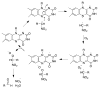
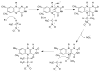
The flavoprotein nitroalkane oxidase catalyzes the oxidation of neutral nitroalkanes to the corresponding aldehydes or ketones, releasing nitrite and transferring electrons to O2 to form H2O2. A combination of solution and structural analyses have provided a detailed understanding of the mechanism of this enzyme.
Keywords: Flavoprotein; Mechanism; Nitroalkane oxidase; Nitronate monooxygenase; Structure.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

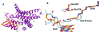
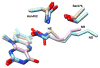
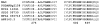
References
-
- Porter DJT, Voet JG, Bright HJ. Nitroalkanes as reductive substrates for flavoprotein oxidases. Z Naturforsch. 1972;27b:1052–1053. - PubMed
-
- Porter DJT, Voet JG, Bright HJ. Direct evidence for carbanions and covalent N5-flavin-carbanion adducts as catalytic intermediates in the oxidation of nitroethane by D-amino acid oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1973;248:4400–4416. - PubMed
-
- Porter DJT, Bright HJ. Mechanism of oxidation of nitroethane by glucose oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1977;252:4361–4370. - PubMed
-
- Kurtz KA, Fitzpatrick PF. pH and secondary kinetic isotope effects on the reaction of D-amino acid oxidase with nitroalkane anions: Evidence for direct attack on the flavin by carbanions. J Am Chem Soc. 1997;119:1155–1156.
-
- Kido T, Yamamoto T, Soda K. Microbial assimilation of alkyl nitro compounds and formation of nitrite. Arch Microbiol. 1975;106:165–169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

