MiR-696 Regulates C2C12 Cell Proliferation and Differentiation by Targeting CNTFRα
- PMID: 28529450
- PMCID: PMC5436562
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.17508
MiR-696 Regulates C2C12 Cell Proliferation and Differentiation by Targeting CNTFRα
Abstract
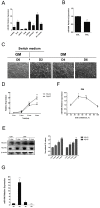
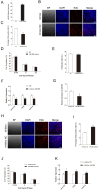
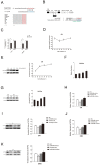
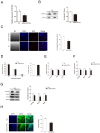
Micro-696 (miR-696) has been previously known as an exercise related miRNA, which has a profound role in fatty acid oxidation and mitochondrial biogenesis of skeletal muscle. However, its role in skeletal myoblast proliferation and differentiation is still unclear. In this study, we found that miR-696 expressed highly in skeletal muscle and reduced during C2C12 myoblasts differentiation. MiR-696 overexpression repressed C2C12 myoblast proliferation and myofiber formation, while knockdown of endogenous miR-696 expression showed opposite results. During myogenesis, we observed an inversed expression pattern between miR-696 and CNTFRα in vitro, and demonstrated that miR-696 could specifically target CNTFRα and repress the expression of CNTFRα. Additionally, we further found that knockdown of CNTFRα suppressed the proliferation and differentiation of C2C12 cells. Taking all things together, we propose a novel insight that miR-696 down-regulates C2C12 cell myogenesis by inhibiting CNTFRα expression.
Keywords: CNTFRα; MiR-696; myoblast proliferation and differentiation..
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Perry RL, Rudnick MA. Molecular mechanisms regulating myogenic determination and differentiation. Frontiers in bioscience: a journal and virtual library. 2000;5:D750–67. - PubMed
-
- Buckingham M, Rigby PW. Gene regulatory networks and transcriptional mechanisms that control myogenesis. Developmental cell. 2014;28:225–38. - PubMed
-
- Hutvagner G, Zamore PD. A microRNA in a multiple-turnover RNAi enzyme complex. Science. 2002;297:2056–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

