Toll-Interacting Protein in Resolving and Non-Resolving Inflammation
- PMID: 28529512
- PMCID: PMC5418219
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00511
Toll-Interacting Protein in Resolving and Non-Resolving Inflammation
Abstract
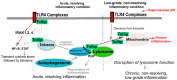
Innate leukocytes manifest dynamic and distinct inflammatory responses upon challenges with rising dosages of pathogen-associated molecular pattern molecules such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS). To differentiate signal strengths, innate leukocytes may utilize distinct intracellular signaling circuitries modulated by adaptor molecules. Toll-interacting protein (Tollip) is one of the critical adaptor molecules potentially playing key roles in modulating the dynamic adaptation of innate leukocytes to varying dosages of external stimulants. While Tollip may serve as a negative regulator of nuclear factor κ of activated B cells signaling pathway in cells challenged with higher dosages of LPS, it acts as a positive regulator for low-grade chronic inflammation in leukocytes programmed by subclinical low-dosages of LPS. This review aims to discuss recent progress in our understanding of complex innate leukocyte dynamics and its relevance in the pathogenesis of resolving versus non-resolving chronic inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: lipopolysaccharide; low-grade inflammation; lysosome fusion; mitochondria; toll-interacting protein; toll-like receptor 4.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Programming and memory dynamics of innate leukocytes during tissue homeostasis and inflammation.J Leukoc Biol. 2017 Sep;102(3):719-726. doi: 10.1189/jlb.6MR0117-027RR. Epub 2017 May 5. J Leukoc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28476750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate-mediated Tollip induction through the 67-kDa laminin receptor negatively regulating TLR4 signaling in endothelial cells.Immunobiology. 2014 Nov;219(11):866-72. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2014.07.010. Epub 2014 Jul 22. Immunobiology. 2014. PMID: 25109435
-
Molecular Mechanisms That Underlie the Dynamic Adaptation of Innate Monocyte Memory to Varying Stimulant Strength of TLR Ligands.Front Immunol. 2016 Nov 10;7:497. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00497. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27891130 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immune programing by endotoxin and its pathological consequences.Front Immunol. 2015 Jan 6;5:680. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00680. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25610440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial lipopolysaccharide induces increased expression of toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 and downstream TLR signaling molecules in bovine mammary epithelial cells.Vet Res. 2008 Mar-Apr;39(2):11. doi: 10.1051/vetres:2007047. Epub 2007 Dec 21. Vet Res. 2008. PMID: 18096120
Cited by
-
BLK positively regulates TLR/IL-1R signaling by catalyzing TOLLIP phosphorylation.J Cell Biol. 2024 Feb 5;223(2):e202302081. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202302081. Epub 2023 Dec 11. J Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38078859 Free PMC article.
-
TOLLIP inhibits lipid accumulation and the integrated stress response in alveolar macrophages to control Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection.Nat Microbiol. 2024 Apr;9(4):949-963. doi: 10.1038/s41564-024-01641-w. Epub 2024 Mar 25. Nat Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38528148 Free PMC article.
-
Year-Long Rhinovirus Infection is Influenced by Atmospheric Conditions, Outdoor Air Virus Presence, and Immune System-Related Genetic Polymorphisms.Food Environ Virol. 2019 Dec;11(4):340-349. doi: 10.1007/s12560-019-09397-x. Epub 2019 Jul 26. Food Environ Virol. 2019. PMID: 31350695
-
Lauric acid promotes neuronal maturation mediated by astrocytes in primary cortical cultures.Heliyon. 2020 May 11;6(5):e03892. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03892. eCollection 2020 May. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 32420479 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological insights and role of bufalin (bufadienolides) in inflammation modulation: a narrative review.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Oct;32(5):3057-3077. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01517-9. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 39012431 Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

