Novel and Effective Therapeutic Regimens for Helicobacter pylori in an Era of Increasing Antibiotic Resistance
- PMID: 28529929
- PMCID: PMC5418237
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00168
Novel and Effective Therapeutic Regimens for Helicobacter pylori in an Era of Increasing Antibiotic Resistance
Abstract
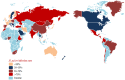
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a common gastrointestinal bacterial strain closely associated with the incidence of chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma, and gastric cancer. A current research and clinical challenge is the increased rate of antibiotic resistance in H. pylori, which has led to a decreased H. pylori eradication rate. In this article, we review recent H. pylori infection and reinfection rates and H. pylori resistance to antibiotics, and we discuss the pertinent treatments. A PubMed literature search was performed using the following keywords: Helicobacter pylori, infection, reinfection, antibiotic resistance, bismuth, proton pump inhibitors, vonoprazan, susceptibility, quintuple therapy, dual therapy, and probiotic. The prevalence of H. pylori has remained high in some areas despite the decreasing trend of H. pylori prevalence observed over time. Additionally, the H. pylori reinfection rate has varied in different countries due to socioeconomic and hygienic conditions. Helicobacter pylori monoresistance to clarithromycin, metronidazole or levofloxacin was common in most countries. However, the prevalence of amoxicillin and tetracycline resistance has remained low. Because H. pylori infection and reinfection present serious challenges and because H. pylori resistance to clarithromycin, metronidazole or levofloxacin remains high in most countries, the selection of an efficient regimen to eradicate H. pylori is critical. Currently, bismuth-containing quadruple therapies still achieve high eradication rates. Moreover, susceptibility-based therapies are alternatives because they may avoid the use of unnecessary antibiotics. Novel regimens, e.g., vonoprazan-containing triple therapies, quintuple therapies, high-dose dual therapies, and standard triple therapies with probiotics, require further studies concerning their efficiency and safety for treating H. pylori.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; infection; reinfection; resistance; treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Anagnostopoulos G. K., Tsiakos S., Margantinis G., Kostopoulos P., Arvanitidis D. (2004). Esomeprazole versus omeprazole for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection: results of a randomized controlled study. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 38, 503–506. 10.1097/01.mcg.0000129061.54277.c6 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical