Coronary Artery Aneurysms: A Review of the Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment
- PMID: 28529940
- PMCID: PMC5418231
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2017.00024
Coronary Artery Aneurysms: A Review of the Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Abstract
Coronary artery aneurysms (CAAs) are uncommon and describe a localized dilatation of a coronary artery segment more than 1.5-fold compared with adjacent normal segments. The incidence of CAAs varies from 0.3 to 5.3%. Ever since the dawn of the interventional era, CAAs have been increasingly diagnosed on coronary angiography. Causative factors include atherosclerosis, Takayasu arteritis, congenital disorders, Kawasaki disease (KD), and percutaneous coronary intervention. The natural history of CAAs remains unclear; however, several recent studies have postulated the underlying molecular mechanisms of CAAs, and genome-wide association studies have revealed several genetic predispositions to CAA. Controversies persist regarding the management of CAAs, and emerging findings support the importance of an early diagnosis in patients predisposed to CAAs, such as in children with KD. This review aims to summarize the present knowledge of CAAs and collate the recent advances regarding the epidemiology, etiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of this disease.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; coronary aneurysm; coronary artery aneursym; coronary artery disease; coronary artery ectasia; coronary stent.
Figures

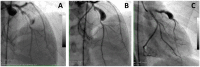
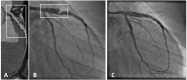
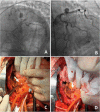
References
-
- Packard M, Wechsler HF. Aneurysms of coronary arteries. Arch Intern Med (1929) 43:1–14. 10.1001/archinte.1929.00130240004001 - DOI
-
- Robertson T, Fisher L. Prognostic significance of coronary artery aneurysm and ectasia in the Coronary Artery Surgery Study (CASS) registry. Prog Clin Biol Res (1987) 250:325–39. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

