Anti-platelet factor 4/polyanion antibodies mediate a new mechanism of autoimmunity
- PMID: 28530237
- PMCID: PMC5458132
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms14945
Anti-platelet factor 4/polyanion antibodies mediate a new mechanism of autoimmunity
Abstract
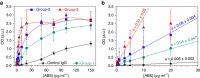
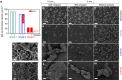
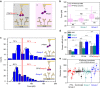
Antibodies recognizing complexes of the chemokine platelet factor 4 (PF4/CXCL4) and polyanions (P) opsonize PF4-coated bacteria hereby mediating bacterial host defense. A subset of these antibodies may activate platelets after binding to PF4/heparin complexes, causing the prothrombotic adverse drug reaction heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT). In autoimmune-HIT, anti-PF4/P-antibodies activate platelets in the absence of heparin. Here we show that antibodies with binding forces of approximately 60-100 pN activate platelets in the presence of polyanions, while a subset of antibodies from autoimmune-HIT patients with binding forces ≥100 pN binds to PF4 alone in the absence of polyanions. These antibodies with high binding forces cluster PF4-molecules forming antigenic complexes which allow binding of polyanion-dependent anti-PF4/P-antibodies. The resulting immunocomplexes induce massive platelet activation in the absence of heparin. Antibody-mediated changes in endogenous proteins that trigger binding of otherwise non-pathogenic (or cofactor-dependent) antibodies may also be relevant in other antibody-mediated autoimmune disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Greinacher A. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. N. Engl. J. Med. 373, 252–261 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Warkentin T. E., Basciano P. A., Knopman J. & Bernstein R. A. Spontaneous heparin-induced thrombocytopenia syndrome: 2 new cases and a proposal for defining this disorder. Blood 123, 3651–3654 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Krauel K. et al.. Platelet factor 4 binds to bacteria, [corrected] inducing antibodies cross-reacting with the major antigen in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood 117, 1370–1378 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Krauel K. et al.. Platelet factor 4 binding to lipid A of Gram-negative bacteria exposes PF4/heparin-like epitopes. Blood 120, 3345–3352 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Kreimann M. et al.. Binding of anti-platelet factor 4/heparin antibodies depends on the thermodynamics of conformational changes in platelet factor 4. Blood 124, 2442–2449 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

