Fifteen new risk loci for coronary artery disease highlight arterial-wall-specific mechanisms
- PMID: 28530674
- PMCID: PMC5555387
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3874
Fifteen new risk loci for coronary artery disease highlight arterial-wall-specific mechanisms
Abstract
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Although 58 genomic regions have been associated with CAD thus far, most of the heritability is unexplained, indicating that additional susceptibility loci await identification. An efficient discovery strategy may be larger-scale evaluation of promising associations suggested by genome-wide association studies (GWAS). Hence, we genotyped 56,309 participants using a targeted gene array derived from earlier GWAS results and performed meta-analysis of results with 194,427 participants previously genotyped, totaling 88,192 CAD cases and 162,544 controls. We identified 25 new SNP-CAD associations (P < 5 × 10-8, in fixed-effects meta-analysis) from 15 genomic regions, including SNPs in or near genes involved in cellular adhesion, leukocyte migration and atherosclerosis (PECAM1, rs1867624), coagulation and inflammation (PROCR, rs867186 (p.Ser219Gly)) and vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation (LMOD1, rs2820315). Correlation of these regions with cell-type-specific gene expression and plasma protein levels sheds light on potential disease mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
AM, EBF and JBW are full time employees of Pfizer. DFF is now a full time employee of Bayer AG, Germany. JD reports personal fees and non-financial support from Merck Sharp & Dohme UK Atherosclerosis, Novartis Cardiovascular & Metabolic Advisory Board, Pfizer Population Research Advisory Panel, Sanofi Advisory Board.
Figures
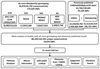
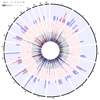
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P30 ES010126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- RG/08/014/24067/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R56 DK104806/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L003120/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- T32 HL098049/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 268834/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- CH/12/2/29428/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R21 HL123677/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- SP/02/002/14543/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- 1508647/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0800270/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K99 HL130580/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- SP/09/002/27676/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- K23 DK088942/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD020069/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- RG/14/5/30893/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

