The microRNA miR-31 inhibits CD8+ T cell function in chronic viral infection
- PMID: 28530712
- PMCID: PMC5753758
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.3755
The microRNA miR-31 inhibits CD8+ T cell function in chronic viral infection
Erratum in
-
Erratum: The microRNA miR-31 inhibits CD8+ T cell function in chronic viral infection.Nat Immunol. 2017 Sep 19;18(10):1173. doi: 10.1038/ni1017-1173d. Nat Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28926530 No abstract available.
Abstract
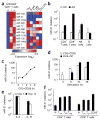
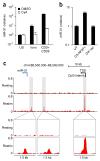
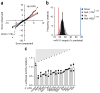
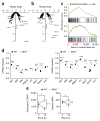
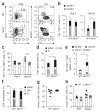
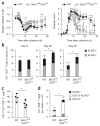
During infection, antigen-specific T cells undergo tightly regulated developmental transitions controlled by transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. We found that the microRNA miR-31 was strongly induced by activation of the T cell antigen receptor (TCR) in a pathway involving calcium and activation of the transcription factor NFAT. During chronic infection with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) clone 13, miR-31-deficent mice recovered from clinical disease, while wild-type mice continued to show signs of disease. This disease phenotype was explained by the presence of larger numbers of cytokine-secreting LCMV-specific CD8+ T cells in miR-31-deficent mice than in wild-type mice. Mechanistically, miR-31 increased the sensitivity of T cells to type I interferons, which interfered with effector T cell function and increased the expression of several proteins related to T cell dysfunction during chronic infection. These studies identify miR-31 as an important regulator of T cell exhaustion in chronic infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
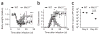
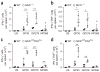
Comment in
-
miR-31: a key player in CD8 T-cell exhaustion.Cell Mol Immunol. 2017 Dec;14(12):954-956. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2017.89. Epub 2017 Sep 11. Cell Mol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28890544 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
MicroRNA 31 inhibits CD8+ T-cell function by increasing its sensitivity to type I interferon signaling in chronic viral infection.Cell Mol Immunol. 2018 May;15(5):533-535. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2017.99. Epub 2017 Oct 2. Cell Mol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 28967879 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Crucial role of miR-31 in induction of CD8+ T-cell exhaustion and reinforcement of type 1 interferon signaling.Cell Mol Immunol. 2018 Jul;15(7):651-653. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2017.96. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Cell Mol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29176744 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
miRNA-31 regulates the CD8 T cell response to type I IFNs during chronic infection.Cell Mol Immunol. 2018 Apr;15(4):402-404. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2017.80. Epub 2017 Sep 4. Cell Mol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29532790 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wherry EJ, et al. Molecular signature of CD8+ T cell exhaustion during chronic viral infection. Immunity. 2007;27:670–684. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

