Morphine for chronic neuropathic pain in adults
- PMID: 28530786
- PMCID: PMC6481499
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011669.pub2
Morphine for chronic neuropathic pain in adults
Abstract
Background: Neuropathic pain, which is caused by a lesion or disease affecting the somatosensory system, may be central or peripheral in origin. Neuropathic pain often includes symptoms such as burning or shooting sensations, abnormal sensitivity to normally painless stimuli, or an increased sensitivity to normally painful stimuli. Neuropathic pain is a common symptom in many diseases of the nervous system. Opioid drugs, including morphine, are commonly used to treat neuropathic pain. Most reviews have examined all opioids together. This review sought evidence specifically for morphine; other opioids are considered in separate reviews.
Objectives: To assess the analgesic efficacy and adverse events of morphine for chronic neuropathic pain in adults.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, and Embase for randomised controlled trials from inception to February 2017. We also searched the reference lists of retrieved studies and reviews, and online clinical trial registries.
Selection criteria: We included randomised, double-blind trials of two weeks' duration or longer, comparing morphine (any route of administration) with placebo or another active treatment for neuropathic pain, with participant-reported pain assessment.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently extracted data and assessed trial quality and potential bias. Primary outcomes were participants with substantial pain relief (at least 50% pain relief over baseline or very much improved on Patient Global Impression of Change scale (PGIC)), or moderate pain relief (at least 30% pain relief over baseline or much or very much improved on PGIC). Where pooled analysis was possible, we used dichotomous data to calculate risk ratio (RR) and number needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome (NNT) or harmful outcome (NNH). We assessed the quality of the evidence using GRADE and created 'Summary of findings' tables.
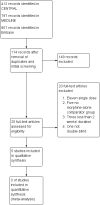
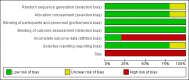
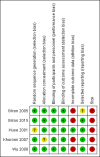
Main results: We identified five randomised, double-blind, cross-over studies with treatment periods of four to seven weeks, involving 236 participants in suitably characterised neuropathic pain; 152 (64%) participants completed all treatment periods. Oral morphine was titrated to maximum daily doses of 90 mg to 180 mg or the maximum tolerated dose, and then maintained for the remainder of the study. Participants had experienced moderate or severe neuropathic pain for at least three months. Included studies involved people with painful diabetic neuropathy, chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia criteria, phantom limb or postamputation pain, and lumbar radiculopathy. Exclusions were typically people with other significant comorbidity or pain from other causes.Overall, we judged the studies to be at low risk of bias, but there were concerns over small study size and the imputation method used for participants who withdrew from the studies, both of which could lead to overestimation of treatment benefits and underestimation of harm.There was insufficient or no evidence for the primary outcomes of interest for efficacy or harm. Four studies reported an approximation of moderate pain improvement (any pain-related outcome indicating some improvement) comparing morphine with placebo in different types of neuropathic pain. We pooled these data in an exploratory analysis. Moderate improvement was experienced by 63% (87/138) of participants with morphine and 36% (45/125) with placebo; the risk difference (RD) was 0.27 (95% confidence interval (CI) 0.16 to 0.38, fixed-effects analysis) and the NNT 3.7 (2.6 to 6.5). We assessed the quality of the evidence as very low because of the small number of events; available information did not provide a reliable indication of the likely effect, and the likelihood that the effect will be substantially different was very high. A similar exploratory analysis for substantial pain relief on three studies (177 participants) showed no difference between morphine and placebo.All-cause withdrawals in four studies occurred in 16% (24/152) of participants with morphine and 12% (16/137) with placebo. The RD was 0.04 (-0.04 to 0.12, random-effects analysis). Adverse events were inconsistently reported, more common with morphine than with placebo, and typical of opioids. There were two serious adverse events, one with morphine, and one with a combination of morphine and nortriptyline. No deaths were reported. These outcomes were assessed as very low quality because of the limited number of participants and events.
Authors' conclusions: There was insufficient evidence to support or refute the suggestion that morphine has any efficacy in any neuropathic pain condition.
Conflict of interest statement
TC: none known.
JC: none known.
PW: none known.
SD: none known.
DBC: none known; DBC is a specialised pain physician and has managed patients with chronic pain.
DA: is a specialist pain physician and manages patients with neuropathic pain. He has received lecture fees from Grünenthal (2014, 2015) and Pfizer (2016).
PC: none known; PC is a specialist pain physician and manages patients with neuropathic pain. PC received support from Boston Scientific (2014) for travel and accommodation at a scientific meeting; Boston Scientific does not market drugs.
RAM: has received grant support from Grünenthal relating to individual patient level analyses of trial data regarding tapentadol in osteoarthritis and back pain (2015). He has received honoraria for attending boards with Menarini concerning methods of analgesic trial design (2014), with Novartis (2014) about the design of network meta‐analyses, and RB on understanding pharmacokinetics of drug uptake (2015). He has received honoraria from Omega Pharma (2016) and Futura Pharma (2016) for providing advice on trial and data analysis methods.
Figures




Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Gilron 2005 {published data only}
Gilron 2015 {published data only}
Huse 2001 {published data only}
Khoromi 2007 {published data only}
References to studies excluded from this review
Attal 2002 {published data only}
-
- Attal N, Guiriman F, Brasseur L, Gaude V, Chauvin M, Bouhassira D. Effects of IV morphine in central pain: a randomized placebo‐controlled study. Neurology 2002;58(4):554‐63. [PUBMED: 11865132] - PubMed
Dellemijn 1994 {published data only}
-
- Dellemijn PL, Verbiest HB, Vliet JJ, Roos PJ, Vecht CJ. Medical therapy of malignant nerve pain. A randomised double‐blind explanatory trial with naproxen versus slow‐release morphine. European Journal of Cancer 1994;30A(9):1244‐50. [PUBMED: 7999406] - PubMed
Domzal 1986 {published data only}
-
- Domzal T, Szymanski H, Zaleska B. Morphine epidural block in lumbosacral pain [Morfinowe blokady nadtwardowkowe w bolu ledzwiowo‐krzyzowym]. Neurologia i Neurochirurgia Polska 1986;20(3):214‐7. [PUBMED: 2946972] - PubMed
Eide 1994 {published data only}
Galer 2005 {published data only}
-
- Galer BS, Lee D, Ma T, Nagle B, Schlagheck TG. MorphiDex (morphine sulfate/dextromethorphan hydrobromide combination) in the treatment of chronic pain: three multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, controlled clinical trials fail to demonstrate enhanced opioid analgesia or reduction in tolerance. Pain 2005;115(3):284‐95. [DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2005.03.004] - DOI - PubMed
Harke 2001 {published data only}
-
- Harke H, Gretenkort P, Ladleif HU, Rahman S, Harke O. The response of neuropathic pain and pain in complex regional pain syndrome I to carbamazepine and sustained‐release morphine in patients pretreated with spinal cord stimulation: a double‐blinded randomized study. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2001;92(2):488‐95. [DOI: 10.1213/00000539-200102000-00039] - DOI - PubMed
Jadad 1992 {published data only}
Kalman 2002 {published data only}
Nalamachu 2013 {published data only}
Patarica‐Huber 2011 {published data only}
-
- Patarica‐Huber E, Boskov N, Pjevic M. Multimodal approach to therapy‐related neuropathic pain in breast cancer. Journal of B.U.ON. 2011;16(1):40‐5. [PUBMED: 21674848] - PubMed
Persson 1998 {published data only}
-
- Persson J, Hasselstrom J, Wiklund B, Heller A, Svensson JO, Gustafsson LL. The analgesic effect of racemic ketamine in patients with chronic ischemic pain due to lower extremity arteriosclerosis obliterans. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavia 1998;42(7):750‐8. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1998.tb05317.x] - DOI - PubMed
Raja 2002 {published data only}
Rocha 2014 {published data only}
Rowbotham 1991 {published data only}
-
- Rowbotham MC, Reisner‐Keller LA, Fields HL. Both intravenous lidocaine and morphine reduce the pain of postherpetic neuralgia. Neurology 1991;41(7):1024‐8. [PUBMED: 1712433] - PubMed
Serinken 2016 {published data only}
Siddall 2000 {published data only}
Wasan 2006 {published data only}
Watt 1996 {published data only}
Wu 2002 {published data only}
Xiong 2008 {published data only}
-
- Xiong J, Liang C, Wu X, Zhao YX, Fu L, Zhou YF. Efficacy and safety of oxycodone‐acetaminophen tablet in 142 patients with different types of moderate and advanced cancer pain. Chinese Journal of New Drugs 2008;17(21):1877‐9. [EMBASE: 2008602294]
Additional references
AlBalawi 2013
Ball 1985
Baron 2012
Baron 2017
Berger 2004
Berger 2009
Berger 2012
Bouhassira 2008
Brok 2009
-
- Brok J, Thorlund K, Wetterslev J, Gluud C. Apparently conclusive meta‐analyses may be inconclusive ‐ Trial Sequential Analysis adjustment of random error risk due to repetitive testing of accumulating data in apparently conclusive neonatal meta‐analyses. International Journal of Epidemiology 2009;38(1):287‐98. [DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyn188] - DOI - PubMed
Calvo 2012
Chaparro 2012
Collins 1998
Colloca 2017
Dechartres 2013
Dechartres 2014
Demant 2014
-
- Demant DT, Lund K, Vollert J, Maier C, Segerdahl M, Finnerup NB, et al. The effect of oxcarbazepine in peripheral neuropathic pain depends on pain phenotype: a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled phenotype‐stratified study. Pain 2014;155(11):2263‐73. [DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2014.08.014] - DOI - PubMed
Derry 2012
Derry 2014
Derry 2016
Derry 2017
Dworkin 2008
Dworkin 2013
Edelsberg 2011
Elbourne 2002
Els 2016
-
- Els C, Hagtvedt R, Kunyk D, Sonnenberg B, Lappi VG, Straube S. High‐dose opioids for chronic non‐cancer pain: an overview of Cochrane reviews. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2016, Issue 7. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012299] - DOI
EPOC 2015
-
- Effective Practice, Organisation of Care (EPOC). 23. Worksheets for preparing a Summary of Findings using GRADE. Resources for review authors, 2015. Oslo: Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services. Available at: epoc.cochrane.org/epoc‐specific‐resources‐review‐authors (accessed 13 February 2017).
Faura 1996
Faura 1998
Finnerup 2013
Finnerup 2015
Franklin 2014
Gaskell 2014
Gaskell 2016
Grahame‐Smith 2002
-
- Grahame‐Smith DG, Aronson JK. Oxford Textbook of Clinical Pharmacology and Drug Therapy. 3rd Edition. Oxford (UK): Oxford University Press, 2002.
Gustorff 2008
Guyatt 2011
Guyatt 2013a
-
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Sultan S, Brozek J, Glasziou P, Alonso‐Coello P, et al. GRADE guidelines: 11. Making an overall rating of confidence in effect estimates for a single outcome and for all outcomes. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013;66:151‐7. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2012.01.006] - DOI - PubMed
Guyatt 2013b
Hall 2008
Hall 2013
Hand 1987
-
- Hand CW, Blunnie WP, Claffey LP, McShane AJ, McQuay HJ, Moore RA. Potential analgesic contribution from morphine‐6‐glucuronide in CSF. Lancet 1987;2(8569):1207‐8. - PubMed
Haroutiunian 2012
Helfert 2015
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Hoffman 2010
Jadad 1996
Jensen 2011
Kalso 2013
Katusic 1991
Klimas 2014
Koopman 2009
L'Abbé 1987
Lange 2010
Lunn 2014
McNicol 2013
McQuay 1998
-
- McQuay H, Moore R. An Evidence‐Based Resource for Pain Relief. Oxford (UK): Oxford University Press, 1998. [ISBN: 0‐19‐263048‐2]
McQuay 2007
-
- McQuay HJ, Smith LA, Moore RA. Chronic pain. In: Stevens A, Raftery J, Mant J, Simpson S editor(s). Health Care Needs Assessment, 3rd Series. Oxford (UK): Radcliffe Publishing, 2007. [ISBN: 978‐1‐84619‐063‐6]
Moore 1998
Moore 2008
-
- Moore RA, Barden J, Derry S, McQuay HJ. Managing potential publication bias. In: McQuay HJ, Kalso E, Moore RA editor(s). Systematic Reviews in Pain Research: Methodology Refined. Seattle (WA): IASP Press, 2008:15‐24. [ISBN: 978‐0‐931092‐69‐5]
Moore 2009
Moore 2010a
Moore 2010b
Moore 2010c
Moore 2010d
Moore 2010e
-
- Moore RA, Moore OA, Derry S, Peloso PM, Gammaitoni AR, Wang H. Responder analysis for pain relief and numbers needed to treat in a meta‐analysis of etoricoxib osteoarthritis trials: bridging a gap between clinical trials and clinical practice. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2010;69(2):374‐9. [DOI: 10.1136/ard.2009.107805] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Moore 2011a
-
- Moore RA, Straube S, Paine J, Derry S, McQuay HJ. Minimum efficacy criteria for comparisons between treatments using individual patient meta‐analysis of acute pain trials: examples of etoricoxib, paracetamol, ibuprofen, and ibuprofen/paracetamol combinations after third molar extraction. Pain 2011;152(5):982‐9. - PubMed
Moore 2011b
Moore 2012
Moore 2013a
Moore 2013b
Moore 2014a
Moore 2014b
Moore 2014c
Moore 2015a
Moore 2015b
Moore 2015c
NICE 2013
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Neuropathic pain ‐ pharmacological management: the pharmacological management of neuropathic pain in adults in non‐specialist settings, 2013 (updated 2017). nice.org.uk/guidance/cg173 (accessed 23 February 2017).
Nüesch 2010
O'Brien 2010
Overall 1969
-
- Overall JE. Classical statistical hypothesis testing within the context of Bayesian theory. Psychological Bulletin 1969;71(4):285‐92. [DOI: 10.1037/h0026860] - DOI
PaPaS 2012
-
- Cochrane Pain, Palliative and Supportive Care Group (PaPaS) author and referee guidance. papas.cochrane.org/papas‐documents (accessed 23 February 2017).
Rappaport 1994
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Rey 1993
-
- Rey R. History of Pain. Paris (France): Editions La Decouverte, 1993. [ISBN: 2‐7071‐2256‐4]
Roberts 2015
Scott 2006
Sear 1989
Sommer 2015
-
- Sommer C, Welsch P, Klose P, Schaefert R, Petzke F, Häuser W. Opioids in chronic neuropathic pain. A systematic review and meta‐analysis of efficacy, tolerability and safety in randomized placebo‐controlled studies of at least 4 weeks duration [Opioide bei chronischem neuropathischem Schmerz]. Schmerz (Berlin, Germany) 2015;29(1):35‐46. [DOI: 10.1007/s00482-014-1455-x] - DOI - PubMed
Soni 2013
Stannard 2016
Straube 2008
-
- Straube S, Derry S, McQuay HJ, Moore RA. Enriched enrolment: definition and effects of enrichment and dose in trials of pregabalin and gabapentin in neuropathic pain. A systematic review. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2008;66(2):266‐75. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2008.03200] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Straube 2010
Sultan 2008
Tayeb 2016
Thorlund 2011
Torrance 2006
Treede 2008
Turner 2013
van Hecke 2014
van Hoek 2009
von Hehn 2012
Vos 2012
-
- Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Michaud C, Ezzati M, et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990‐2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012;380(9859):2163‐96. [DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
WHO 1986
-
- World Health Organization. Cancer Pain Relief, 1986. who.int/iris/handle/10665/43944. Geneva: WHO, (accessed 23 February 2017).
WHO 2011
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Essential Medicines List 17th edition, 2011. whqlibdoc.who.int/hq/2011/a95053_eng.pdf (accessed 23 February 2017).
Wiffen 2013
Wiffen 2015
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

