Multitargeted Imidazoles: Potential Therapeutic Leads for Alzheimer's and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases
- PMID: 28530811
- PMCID: PMC5483893
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00475
Multitargeted Imidazoles: Potential Therapeutic Leads for Alzheimer's and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
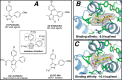
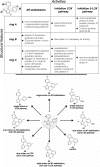
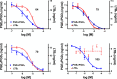
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a complex, multifactorial disease in which different neuropathological mechanisms are likely involved, including those associated with pathological tau and Aβ species as well as neuroinflammation. In this context, the development of single multitargeted therapeutics directed against two or more disease mechanisms could be advantageous. Starting from a series of 1,5-diarylimidazoles with microtubule (MT)-stabilizing activity and structural similarities with known NSAIDs, we conducted structure-activity relationship studies that led to the identification of multitargeted prototypes with activities as MT-stabilizing agents and/or inhibitors of the cyclooxygenase (COX) and 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) pathways. Several examples are brain-penetrant and exhibit balanced multitargeted in vitro activity in the low μM range. As brain-penetrant MT-stabilizing agents have proven effective against tau-mediated neurodegeneration in animal models, and because COX- and 5-LOX-derived eicosanoids are thought to contribute to Aβ plaque deposition, these 1,5-diarylimidazoles provide tools to explore novel multitargeted strategies for AD and other neurodegenerative diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A rat air pouch model for evaluating the efficacy and selectivity of 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors.Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 Apr 14;584(1):166-74. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.01.021. Epub 2008 Feb 5. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18295198
-
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel 1,2-diaryl-4-substituted-benzylidene-5(4H)-imidazolone derivatives as cytotoxic agents and COX-2/LOX inhibitors.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2018 Apr;351(3-4):e1700311. doi: 10.1002/ardp.201700311. Epub 2018 Feb 5. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2018. PMID: 29400411
-
New hybrid molecules combining benzothiophene or benzofuran with rhodanine as dual COX-1/2 and 5-LOX inhibitors: Synthesis, biological evaluation and docking study.Bioorg Chem. 2017 Jun;72:102-115. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2017.03.012. Epub 2017 Mar 31. Bioorg Chem. 2017. PMID: 28390993
-
Dual acting anti-inflammatory drugs: a reappraisal.Pharmacol Res. 2001 Dec;44(6):437-50. doi: 10.1006/phrs.2001.0872. Pharmacol Res. 2001. PMID: 11735348 Review.
-
New anti-inflammatory treatment strategy in Alzheimer's disease.Jpn J Pharmacol. 2000 Feb;82(2):85-94. doi: 10.1254/jjp.82.85. Jpn J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10877525 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of imidazole-based GSK-3β inhibitors for transdifferentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells to neurons: A potential single-molecule neurotherapeutic foresight.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Dec 15;15:1002419. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.1002419. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36590911 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of polysubstituted imidazoles using AC-SO3H/[Urea]7[ZnCl2]2 as an efficient catalyst system: a novel method, and α-glucosidase inhibitor activity.RSC Adv. 2023 Apr 20;13(18):12455-12463. doi: 10.1039/d3ra00755c. eCollection 2023 Apr 17. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37091625 Free PMC article.
-
Congeners Derived from Microtubule-Active Phenylpyrimidines Produce a Potent and Long-Lasting Paralysis of Schistosoma mansoni In Vitro.ACS Infect Dis. 2021 May 14;7(5):1089-1103. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00508. Epub 2020 Oct 31. ACS Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33135408 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-Penetrant Triazolopyrimidine and Phenylpyrimidine Microtubule Stabilizers as Potential Leads to Treat Human African Trypanosomiasis.ChemMedChem. 2018 Sep 6;13(17):1751-1754. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201800404. Epub 2018 Aug 7. ChemMedChem. 2018. PMID: 29969537 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling Alzheimer's disease: insights from single-cell sequencing and spatial transcriptomic.Front Neurol. 2024 Dec 17;15:1515981. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1515981. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39741706 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Makani V.; Zhang B.; Han H.; Yao Y.; Lassalas P.; Lou K.; Paterson I.; Lee V. M. Y.; Trojanowski J. Q.; Ballatore C.; Smith A. B. III; Brunden K. R. Evaluation of the brain-penetrant microtubule-stabilizing agent, dictyostatin, in the PS19 tau transgenic mouse model of tauopathy. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2016, 4, 106.10.1186/s40478-016-0378-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang B.; Carroll J.; Trojanowski J. Q.; Yao Y.; Iba M.; Potuzak J. S.; Hogan A. M.; Xie S. X.; Ballatore C.; Smith A. B. III; Lee V. M.; Brunden K. R. The microtubule-stabilizing agent, epothilone D, reduces axonal dysfunction, neurotoxicity, cognitive deficits, and Alzheimer-like pathology in an interventional study with aged tau transgenic mice. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 3601–3611. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4922-11.2012. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Medical
Research Materials

