Eyes of Things
- PMID: 28531141
- PMCID: PMC5470918
- DOI: 10.3390/s17051173
Eyes of Things
Abstract
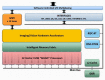
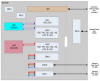
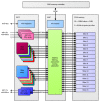
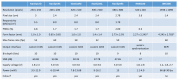
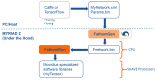
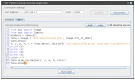
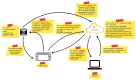
Embedded systems control and monitor a great deal of our reality. While some "classic" features are intrinsically necessary, such as low power consumption, rugged operating ranges, fast response and low cost, these systems have evolved in the last few years to emphasize connectivity functions, thus contributing to the Internet of Things paradigm. A myriad of sensing/computing devices are being attached to everyday objects, each able to send and receive data and to act as a unique node in the Internet. Apart from the obvious necessity to process at least some data at the edge (to increase security and reduce power consumption and latency), a major breakthrough will arguably come when such devices are endowed with some level of autonomous "intelligence". Intelligent computing aims to solve problems for which no efficient exact algorithm can exist or for which we cannot conceive an exact algorithm. Central to such intelligence is Computer Vision (CV), i.e., extracting meaning from images and video. While not everything needs CV, visual information is the richest source of information about the real world: people, places and things. The possibilities of embedded CV are endless if we consider new applications and technologies, such as deep learning, drones, home robotics, intelligent surveillance, intelligent toys, wearable cameras, etc. This paper describes the Eyes of Things (EoT) platform, a versatile computer vision platform tackling those challenges and opportunities.
Keywords: Internet of Things; computer vision; embedded computer vision; eyes of things.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
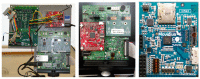
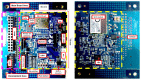
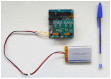
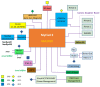








References
-
- Moloney D., Suarez O.D. A Vision for the Future [Soapbox] IEEE Consum. Electron. Mag. 2015;4:40–45. doi: 10.1109/MCE.2015.2392956. - DOI
-
- Markets and Markets . Artificial Intelligence Market by Technology (Deep Learning, Robotics, Digital Personal Assistant, Querying Method, Natural Language Processing, Context Aware Processing), Offering, End-User Industry, and Geography—Global Forecast to 2022. Markets and Markets; Maharashtra, India: 2016.
-
- EoT Project. [(accessed on 18 May 2017)]; Available online: http://eyesofthings.eu.
-
- Akyildiz I.F., Melodia T., Chowdury K.R. Wireless multimedia sensor networks: A survey. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2007;14:32–39. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2007.4407225. - DOI
-
- Farooq M.O., Kunz T. Wireless Multimedia Sensor Networks Testbeds and State-of-the-Art Hardware: A Survey. In: Kim T.H., Adeli H., Fang W.C., Vasilakos T., Stoica A., Patrikakis C.Z., Zhao G., Villalba J.G., Xiao Y., editors. Communication and Networking: International Conference, FGCN 2011, Held as Part of the Future Generation Information Technology Conference, FGIT 2011, in Conjunction with GDC 2011, Jeju Island, Korea, 8–10 December 2011. Proceedings, Part I. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2012. pp. 1–14.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

