Mechanisms governing inflammasome activation, assembly and pyroptosis induction
- PMID: 28531279
- PMCID: PMC5890894
- DOI: 10.1093/intimm/dxx018
Mechanisms governing inflammasome activation, assembly and pyroptosis induction
Abstract
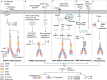
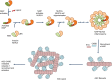
Inflammasomes are multimeric protein complexes that regulate inflammatory responses and pyroptotic cell death to exert host defense against microbes. Intracellular pattern-recognition receptors such as nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat receptors (NLRs) and absent in melanoma 2 like receptors (ALRs) assemble the inflammasome complexes in response to pathogens and danger or altered-self signals in the cell. Inflammasome sensors, in association with an adaptor protein-apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase-activation and -recruitment domain (ASC)-activate inflammatory caspase-1 to enable the release of inflammatory cytokines and induce cell death, conferring host defense against pathogens. Beyond infectious diseases, the importance of inflammasomes is implicated in a variety of clinical conditions such as auto-inflammatory diseases, neuro-degeneration and metabolic disorders and the development of cancers. Understanding inflammasome activation and its molecular regulation can unveil therapeutic targets for controlling inflammasome-mediated disorders. In this review, we describe recent advances in inflammasome biology and discuss its activation, structural insights into inflammasome assembly and mechanisms for the execution of pyroptosis.
Keywords: ASC; NLRs; caspase-1; cell death; pathogens.
© The Japanese Society for Immunology. 2017. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

