Glutamate excitotoxicity induced by orally administered propionic acid, a short chain fatty acid can be ameliorated by bee pollen
- PMID: 28532421
- PMCID: PMC5440900
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-017-0485-7
Glutamate excitotoxicity induced by orally administered propionic acid, a short chain fatty acid can be ameliorated by bee pollen
Abstract
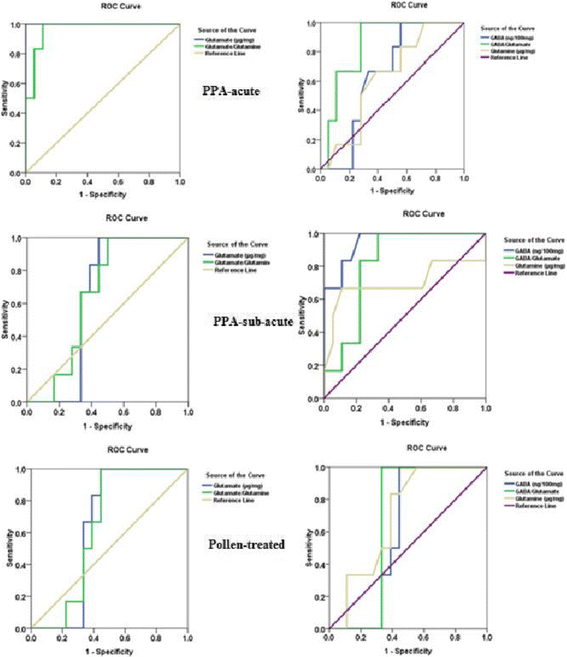
Background: Rodent models may guide investigations towards identifying either environmental neuro-toxicants or drugs with neuro-therapeutic effects. This work aims to study the therapeutic effects of bee pollen on brain glutamate excitotoxicity and the impaired glutamine-glutamate- gamma amino butyric acid (GABA) circuit induced by propionic acid (PPA), a short chain fatty acid, in rat pups.
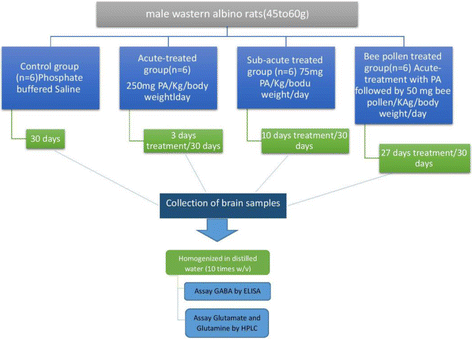
Methods: Twenty-four young male Western Albino rats 3-4 weeks of age, and 45-60 g body weight were enrolled in the present study. They were grouped into four equal groups: Group 1, the control received phosphate buffered saline at the same time of PPA adminstration; Group 2, received 750 mg/kg body weight divided into 3 equal daily doses and served as acute neurotoxic dose of PPA; Group 3, received 750 mg/kg body weight divided in 10 equal doses of 75 mg/kg body weight/day, and served as the sub-acute group; and Group 4, the therapeutic group, was treated with bee pollen (50 mg/kg body weight) for 30 days after acute PPA intoxication. GABA, glutamate and glutamine were measured in the brain homogenates of the four groups.
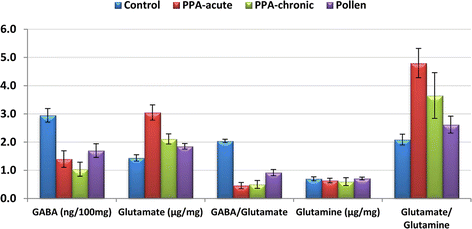
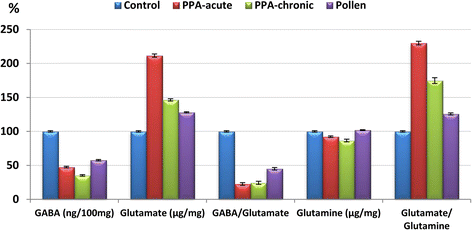
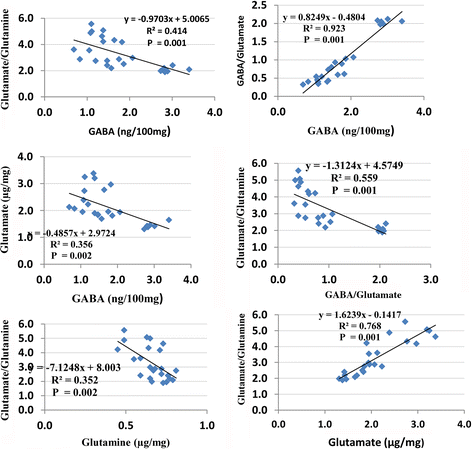
Results: The results showed that PPA caused multiple signs of excitotoxicity, as measured by the elevation of glutamate and the glutamate/glutamine ratio and the decrease of GABA, glutamine and the GABA/glutamate ratio. Bee pollen was effective in counteracting the neurotoxic effects of PPA to a certain extent.
Conclusion: In conclusion, bee pollen demonstrates ameliorating effects on glutamate excitotoxicity and the impaired glutamine-glutamate-GABA circuit as two etiological mechanisms in PPA-induced neurotoxicity.
Keywords: Bee pollen; GABA; Glutamate excitotoxicity; Glutamine; Propionic acid.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Testing the combined effects of probiotics and prebiotics against neurotoxic effects of propionic acid orally administered to rat pups.Food Sci Nutr. 2021 Jun 23;9(8):4440-4451. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2418. eCollection 2021 Aug. Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34401092 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potency of bee pollen against biochemical autistic features induced through acute and sub-acute neurotoxicity of orally administered propionic acid.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Apr 23;16:120. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1099-8. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 27107819 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotic treatment reduces the autistic-like excitation/inhibition imbalance in juvenile hamsters induced by orally administered propionic acid and clindamycin.Metab Brain Dis. 2018 Aug;33(4):1155-1164. doi: 10.1007/s11011-018-0212-8. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Metab Brain Dis. 2018. PMID: 29582256
-
The glutamine-glutamate/GABA cycle: function, regional differences in glutamate and GABA production and effects of interference with GABA metabolism.Neurochem Res. 2015 Feb;40(2):402-9. doi: 10.1007/s11064-014-1473-1. Epub 2014 Nov 8. Neurochem Res. 2015. PMID: 25380696 Review.
-
The glutamate/GABA-glutamine cycle: aspects of transport, neurotransmitter homeostasis and ammonia transfer.J Neurochem. 2006 Aug;98(3):641-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03913.x. Epub 2006 Jun 19. J Neurochem. 2006. PMID: 16787421 Review.
Cited by
-
Testing the combined effects of probiotics and prebiotics against neurotoxic effects of propionic acid orally administered to rat pups.Food Sci Nutr. 2021 Jun 23;9(8):4440-4451. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2418. eCollection 2021 Aug. Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34401092 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling sex-based differences in developing propionic acid-induced features in mice as a rodent model of ASD.PeerJ. 2023 Jun 13;11:e15488. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15488. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37334116 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Novavit in ameliorating the neurotoxicity of propionic acid.Transl Neurosci. 2020 May 26;11(1):134-146. doi: 10.1515/tnsci-2020-0103. eCollection 2020. Transl Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33312719 Free PMC article.
-
Daily Early-Life Exposures to Diet Soda and Aspartame Are Associated with Autism in Males: A Case-Control Study.Nutrients. 2023 Aug 29;15(17):3772. doi: 10.3390/nu15173772. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37686804 Free PMC article.
-
Bee Collected Pollen and Bee Bread: Bioactive Constituents and Health Benefits.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Nov 20;8(12):568. doi: 10.3390/antiox8120568. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31756937 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rosa SG, Quines CB, Stangherlin EC, Nogueira CW. Diphenyl diselenide ameliorates monosodium glutamate induced anxiety-like behavior in rats by modulating hippocampal BDNF-Akt pathway and uptake of GABA and serotonin neurotransmitters. Physiol Behav. 2016;155:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2015.11.038. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

