The effects of a treatment combination of anti-VEGF injections, laser coagulation and cryotherapy on patients with type 3 Coat's disease
- PMID: 28532448
- PMCID: PMC5440965
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-017-0469-4
The effects of a treatment combination of anti-VEGF injections, laser coagulation and cryotherapy on patients with type 3 Coat's disease
Abstract
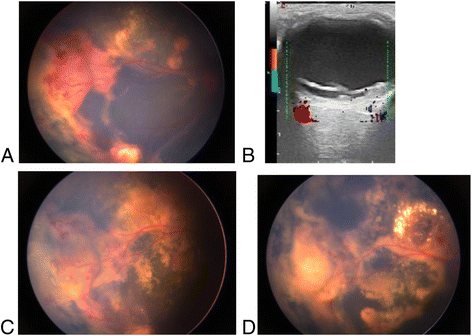
Background: To examined the curative effect of vitreous injection with ranibizumab,laser coagulation and cryotherapy in treating stage 3 Coats' disease with exudative retinal detachment.
Methods: Seventeen patients with stage 3 Coats' disease were enrolled in the study. All eyes were treated with vitreous injection of ranibizumab as initial treatment, and subsequent treatment depended on the absorption of subretinal fluid, Including cryotherapy and laser photocoagulation. Repeat treatment for the two treatment intervals occurred in ≥1 month. The mean follow-up time was 24.12 ± 5.99 months. The main data evaluation and outcome measurements included the patient's vision, intraocular pressure(IOP), optical coherence tomography (OCT), slit lamp examination, indirect ophthalmoscopy, color Doppler imaging (CDI) and color fundus image analysis. The following variables were compared between groups: abnormal vascular changes, subretinal fluid and exudate absorption, retinal reattachment and complications. The final follow-up results were used to determine the effectiveness of treatment.
Results: Of the 17 patients included, 88.24% were male and 11.76% were female. Visual acuity was less than 0.02 in 12 eyes before surgery and 8 eyes after surgery. Visual acuity improved in 7 eyes, accounting for 41.18% of cases, and remained unchanged in 7 eyes, accounting for 41.18% of cases. Three patients were too young to undergo the operation, accounting for 17.65% of cases. The best vision was 0.1. Patients were treated 1 to 5 times for an average of 2.82 ± 0.95 times each. There was no statistically significant difference (t = 1.580, p = 0.135) between the preoperative and postoperative intraocular pressures. However, there was a statistically significant difference between the preoperative and postoperative retinal detachment height (2- related samples Wilcoxon signed rank test with z = 3.517, p = 0.000). The results further showed that all patients had different degrees of subretinal fluid absorption, and some of the new blood vessels subsided. All patients were successfully treated with laser and cryosurgery. No ocular or systemic complications were observed during follow-up.
Conclusions: Intravitreal ranibizumab (IVR), laser coagulation and cryotherapy were effective in the treatment of Coats' disease with exudative retinal detachment.
Trial registration number: We retrospectively registered our study, The trial registration number (TRN) is ChiCTR-ONC-17011161 and date of registration is April 16, 2017.
Keywords: Coats’disease; Ranibizumab; Retinal detachment; Treatment.
Figures


References
-
- Coats G. Forms of retinal dysplasia with massive exudation. R Lond Ophthalmol Hosp Rep. 1908;17:440–525.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

