The Variable Influence of Dispersant on Degradation of Oil Hydrocarbons in Subarctic Deep-Sea Sediments at Low Temperatures (0-5 °C)
- PMID: 28533547
- PMCID: PMC5440406
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-02475-9
The Variable Influence of Dispersant on Degradation of Oil Hydrocarbons in Subarctic Deep-Sea Sediments at Low Temperatures (0-5 °C)
Abstract
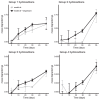
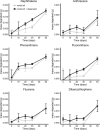
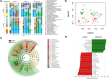
The microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons at low temperatures was investigated in subarctic deep-sea sediments in the Faroe Shetland Channel (FSC). The effect of the marine oil dispersant, Superdispersant 25 on hydrocarbon degradation was also examined. Sediments collected at 500 and 1000 m depth were spiked with a model oil containing 20 hydrocarbons and incubated at ambient temperature (5 and 0 °C, respectively) with and without marine dispersant. Treatment of sediments with hydrocarbons resulted in the enrichment of Gammaproteobacteria, and specifically the genera Pseudoalteromonas, Pseudomonas, Halomonas, and Cobetia. Hydrocarbon degradation was faster at 5 °C (500 m) with 65-89% of each component degraded after 50 days compared to 0-47% degradation at 0 °C (1000 m), where the aromatic hydrocarbons fluoranthene, anthracene, and Dibenzothiophene showed no degradation. Dispersant significantly increased the rate of degradation at 1000 m, but had no effect at 500 m. There was no statistically significant effect of Superdispersant 25 on the bacterial community structure at either station. These results show that the indigenous bacterial community in the FSC has the capacity to mitigate some of the effects of a potential oil spill, however, the effect of dispersant is ambiguous and further research is needed to understand the implications of its use.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria in deep-water subarctic sediments (Faroe-Shetland Channel).J Appl Microbiol. 2018 Oct;125(4):1040-1053. doi: 10.1111/jam.14030. Epub 2018 Jul 24. J Appl Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29928773 Free PMC article.
-
Role of EPS, Dispersant and Nutrients on the Microbial Response and MOS Formation in the Subarctic Northeast Atlantic.Front Microbiol. 2017 Apr 21;8:676. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00676. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28484435 Free PMC article.
-
Simulating pathways of subsurface oil in the Faroe-Shetland Channel using an ocean general circulation model.Mar Pollut Bull. 2017 Jan 15;114(1):315-326. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.09.041. Epub 2016 Oct 13. Mar Pollut Bull. 2017. PMID: 27745973
-
[Evolution of hydrocarbons and bacterial activity in the marine sediments contaminated by crude oil overflow and treated].Int J Environ Anal Chem. 1987;29(3):153-78. doi: 10.1080/03067318708079834. Int J Environ Anal Chem. 1987. PMID: 3596891 French.
-
Chemical Dispersant Enhances Microbial Exopolymer (EPS) Production and Formation of Marine Oil/Dispersant Snow in Surface Waters of the Subarctic Northeast Atlantic.Front Microbiol. 2019 Mar 20;10:553. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00553. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30949150 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pressure and temperature effects on deep-sea hydrocarbon-degrading microbial communities in subarctic sediments.Microbiologyopen. 2019 Jun;8(6):e00768. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.768. Epub 2018 Nov 16. Microbiologyopen. 2019. PMID: 30444300 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of oil, dispersant, and pressure on microbial communities from the Gulf of Mexico.Sci Rep. 2020 Apr 27;10(1):7079. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63190-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32341378 Free PMC article.
-
Inter- and Intra-Annual Bacterioplankton Community Patterns in a Deepwater Sub-Arctic Region: Persistent High Background Abundance of Putative Oil Degraders.mBio. 2021 Mar 16;12(2):e03701-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03701-20. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33727364 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of spatial origin and hydrocarbon composition on bacterial consortia community structure and hydrocarbon biodegradation rates.FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2018 Sep 1;94(9):fiy127. doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiy127. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2018. PMID: 29982504 Free PMC article.
-
Bioaerosol biomonitoring: Sampling optimization for molecular microbial ecology.Mol Ecol Resour. 2019 May;19(3):672-690. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.13002. Mol Ecol Resour. 2019. PMID: 30735594 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cordes EE, et al. Environmental Impacts of the Deep-Water Oil and Gas Industry: A Review to Guide Management Strategies. Front. Environ. Sci. 2016;4:58. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2016.00058. - DOI
-
- Karickhoff S, Brown D, Scott T. Sorption of hydrophobic pollutants on natural sediments. Water Res. 1979;13:241–248. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(79)90201-X. - DOI
-
- Eadie BJ, Landrum PF, Faust W. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments, pore water and the amphipod Pontoporeia hoyi from Lake Michigan. Chemosphere. 1982;11:847–858. doi: 10.1016/0045-6535(82)90131-X. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

