Reduced foot pain after spasticity control with alcohol block in a patient with chronic hemiparetic stroke: a case report
- PMID: 28533627
- PMCID: PMC5430290
- DOI: 10.1589/jpts.29.767
Reduced foot pain after spasticity control with alcohol block in a patient with chronic hemiparetic stroke: a case report
Abstract
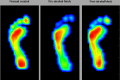
[Purpose] This study report a case of a patient with hemiparetic stroke who showed significantly reduced foot pain when ankle spasticity was reduced using nerve and motor point blocks with 20% ethyl alcohol. [Subject and Methods] A 58-year-old woman with left hemiparesis following intracranial hemorrhage five years previously presented with pain in the left fifth metatarsal head for two years (numeric rating scale[NRS]: 8). Erythema and edema were observed on the lateral aspect of the head of the fifth metatarsal bone. She was diagnosed with a Tailor's bunion. Spasticity was observed in the left ankle plantar flexor and ankle supinator (Modified Ashworth Scale: 1+). Using 20% ethyl alcohol, a block in the medial and lateral motor branches to the gastrocnemius muscle of the left tibial nerve and the motor point of the left posterior tibialis muscle was performed. [Results] After the alcohol block, spasticity had almost disappeared and foot pain was significantly reduced (NRS: 1). Results from the foot pressure measurement system test showed foot contact pressure was highly distributed to the lateral forefoot pre-block. After the block, the distribution of foot contract pressure was similar to normal distribution. [Conclusion] Clinicians should consider the possibility that spasticity can contribute to foot pain.
Keywords: Alcohol block; Spasticity; Tailor’s bunion.
Figures

References
-
- Gallichio JE: Pharmacologic management of spasticity following stroke. Phys Ther, 2004, 84: 973–981. - PubMed
-
- Keenan MA: The management of spastic equinovarus deformity following stroke and head injury. Foot Ankle Clin, 2011, 16: 499–514. - PubMed
-
- Kaplan PE: Rehabilitation of stroke. Burlington: Butterworth-Heinemann, 2003, pp 158–159.
-
- Jang SH, Ahn SH, Park SM, et al. : Alcohol neurolysis of tibial nerve motor branches to the gastrocnemius muscle to treat ankle spasticity in patients with hemiplegic stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil, 2004, 85: 506–508. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
