Unusual Presentation of Rare Cardiac Tumor: The Role of F-18-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography
- PMID: 28533653
- PMCID: PMC5439190
- DOI: 10.4103/0972-3919.202233
Unusual Presentation of Rare Cardiac Tumor: The Role of F-18-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography
Abstract
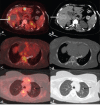
Primary cardiac tumors are rare with angiosarcoma being the most common among malignant cardiac tumor. We present a case of 30-year-old female patient in whom F-18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography demonstrated a necrotic mass in right atrium with multiple fluorodeoxyglucose avid lesions in both upper and lower alveolus, liver, multiple bones, and bilateral lungs. Patient underwent biopsy from gum swelling which revealed metastatic angiosarcoma.
Keywords: Angiosarcoma; F-18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography; gingival metastasis; primary cardiac tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Burke A, Virmani S. Atlas of tumor pathology. Washington, DC: Washington Armed Force Institute of Tumor Pathology; 1996.
-
- Reynen K. Cardiac myxomas. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1610–17. - PubMed
-
- Kambiz R, Harald S, Michael S, Lars S, Andreas H, Tilmann S, et al. Differentiation of malignant and benign cardiac tumors using 18F-FDG PET/CT. J Nucl Med. 2012;53:856–63. - PubMed
-
- Bilski M, Kaminski G, Dziuk M. Metabolic activity assessment of cardiac angiosarcoma by 18FDG PET-CT. Nucl Med Rev Cent East Eur. 2012;15:83–4. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

