Effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate, major ingredient of green tea, on the pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin in healthy volunteers
- PMID: 28533679
- PMCID: PMC5431696
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S130050
Effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate, major ingredient of green tea, on the pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin in healthy volunteers
Abstract
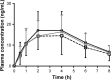
Previous in vitro studies have demonstrated the inhibitory effect of green tea on drug transporters. Because rosuvastatin, a lipid-lowering drug widely used for the prevention of cardiovascular events, is a substrate for many drug transporters, there is a possibility that there is interaction between green tea and rosuvastatin. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of green tea on the pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin in healthy volunteers. An open-label, three-treatment, fixed-sequence study was conducted. On Day 1, 20 mg of rosuvastatin was given to all subjects. After a 3-day washout period, the subjects received 20 mg of rosuvastatin plus 300 mg of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), a major ingredient of green tea (Day 4). After a 10-day pretreatment of EGCG up to Day 14, they received rosuvastatin (20 mg) plus EGCG (300 mg) once again (Day 15). Blood samples for the pharmacokinetic assessments were collected up to 8 hours after each dose of rosuvastatin. A total of 13 healthy volunteers were enrolled. Compared with the administration of rosuvastatin alone, the concomitant use at Day 4 significantly reduced the area under the concentration-time curve from time 0 to the last measurable time (AUClast) by 19% (geometric mean ratio 0.81, 90% confidence interval [CI] 0.67-0.97) and the peak plasma concentration (Cmax) by 15% (geometric mean ratio 0.85, 90% CI 0.70-1.04). AUClast or Cmax of rosuvastatin on Day 15 was not significantly different from that on Day 1. This study demonstrated that co-administration of EGCG reduces the systemic exposure of rosuvastatin by 19%, and pretreatment of EGCG can eliminate that effect of co-administration of EGCG.
Keywords: EGCG; drug interaction; drug transporter; green tea; pharmacokinetics; rosuvastatin.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Werba JP, Misaka S, Giroli MG, et al. Overview of green tea interaction with cardiovascular drugs. Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(9):1213–1219. - PubMed
-
- Amiot MJ, Riva C, Vinet A. Effects of dietary polyphenols on metabolic syndrome features in humans: a systematic review. Obes Rev. 2016;17(7):573–586. - PubMed
-
- Kuriyama S, Shimazu T, Ohmori K, et al. Green tea consumption and mortality due to cardiovascular disease, cancer, and all causes in Japan: the Ohsaki study. JAMA. 2006;296(10):1255–1265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

