Leptin Induces Mitosis and Activates the Canonical Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Neurogenic Regions of Xenopus Tadpole Brain
- PMID: 28533765
- PMCID: PMC5421298
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2017.00099
Leptin Induces Mitosis and Activates the Canonical Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Neurogenic Regions of Xenopus Tadpole Brain
Abstract
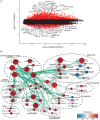
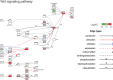
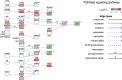
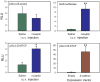
In addition to its well-known role as an adipostat in adult mammals, leptin has diverse physiological and developmental actions in vertebrates. Leptin has been shown to promote development of hypothalamic circuits and to induce mitosis in different brain areas of mammals. We investigated the ontogeny of leptin mRNA, leptin actions on cell proliferation in the brain, and gene expression in the preoptic area/hypothalamus of tadpoles of Xenopus laevis. The level of leptin mRNA was low in premetamorphic tadpoles, but increased strongly at the beginning of metamorphosis and peaked at metamorphic climax. This increase in leptin mRNA at the onset of metamorphosis correlated with increased cell proliferation in the neurogenic zones of tadpole brain. We found that intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) injection of recombinant Xenopus leptin (rxLeptin) in premetamorphic tadpoles strongly increased cell proliferation in neurogenic zones throughout the tadpole brain. We conducted gene expression profiling of genes induced at 2 h following i.c.v. injection of rxLeptin. This analysis identified 2,322 genes induced and 1,493 genes repressed by rxLeptin. The most enriched Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes term was the canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Using electroporation-mediated gene transfer into tadpole brain of a reporter vector responsive to the canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, we found that i.c.v. rxLeptin injection activated Wnt/β-catenin-dependent transcriptional activity. Our findings show that leptin acts on the premetamorphic tadpole brain to induce cell proliferation, possibly acting via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Keywords: Wnt/β-catenin; Xenopus; leptin; metamorphosis; neurogenesis.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

