Control of gene expression through the nonsense-mediated RNA decay pathway
- PMID: 28533900
- PMCID: PMC5437625
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-017-0153-7
Control of gene expression through the nonsense-mediated RNA decay pathway
Abstract
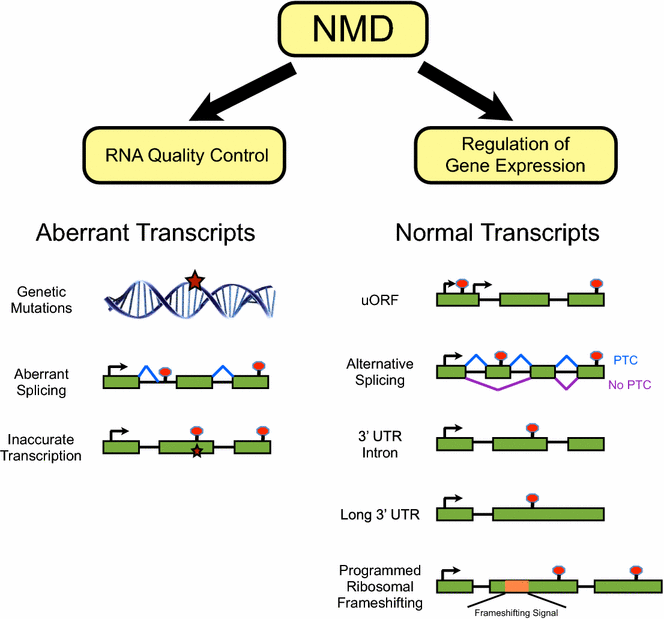
Nonsense-mediated RNA decay (NMD) was originally discovered as a cellular surveillance pathway that safeguards the quality of mRNA transcripts in eukaryotic cells. In its canonical function, NMD prevents translation of mutant mRNAs harboring premature termination codons (PTCs) by targeting them for degradation. However, recent studies have shown that NMD has a much broader role in gene expression by regulating the stability of many normal transcripts. In this review, we discuss the function of NMD in normal physiological processes, its dynamic regulation by developmental and environmental cues, and its association with human disease.
Keywords: Gene expression; Human disease; Nonsense-mediated decay; RNA surveillance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2012 Nov-Dec;3(6):807-28. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1137. Epub 2012 Oct 1. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2012. PMID: 23027648 Review.
-
Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay in Development, Stress and Cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1157:41-83. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-19966-1_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31342437
-
Arginine CGA codons as a source of nonsense mutations: a possible role in multivariant gene expression, control of mRNA quality, and aging.Mol Genet Genomics. 2017 Oct;292(5):1013-1026. doi: 10.1007/s00438-017-1328-y. Epub 2017 May 18. Mol Genet Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28523359
-
The role of alternative splicing coupled to nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in human disease.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2017 Oct;91(Pt B):168-175. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2017.07.013. Epub 2017 Jul 22. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28743674 Review.
-
Defining nonsense-mediated mRNA decay intermediates in human cells.Methods. 2019 Feb 15;155:68-76. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2018.12.005. Epub 2018 Dec 19. Methods. 2019. PMID: 30576707 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The mRNA repressor TRIM71 cooperates with Nonsense-Mediated Decay factors to destabilize the mRNA of CDKN1A/p21.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Dec 16;47(22):11861-11879. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz1057. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31732746 Free PMC article.
-
MS0621, a novel small-molecule modulator of Ewing sarcoma chromatin accessibility, interacts with an RNA-associated macromolecular complex and influences RNA splicing.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 30;13:1099550. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1099550. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36793594 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-Based Strategies for Cancer Therapy: In Silico Design and Evaluation of ASOs for Targeted Exon Skipping.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 3;24(19):14862. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914862. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834310 Free PMC article.
-
Kinome-wide siRNA screen identifies a DCLK2-TBK1 oncogenic signaling axis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Mol Cell. 2024 Feb 15;84(4):776-790.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.12.010. Epub 2024 Jan 10. Mol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38211588 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a candidate gene for the I locus determining the dominant white bulb color in onion (Allium cepa L.).Theor Appl Genet. 2024 May 6;137(6):118. doi: 10.1007/s00122-024-04626-9. Theor Appl Genet. 2024. PMID: 38709404
References
-
- Mcllwain DR, Pan Q, Reilly PT, Elia AJ, McCracken S, Wakeham AC, Itie-Youten A, Blencowe BJ, Mak TW. SMG1 is required for embryogenesis and regulates diverse genes via alternative splicing coupled to nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:12186–12191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1007336107. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Weischenfeldt J, Damgaard I, Bryder D, Theilgaard-Monch K, Thoren LA, Nielsen FC, Jacobsen SE, Nerlov C, Porse BT. NMD is essential for hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells and for eliminating by-products of programmed DNA rearrangements. Genes Dev. 2008;22:1381–1396. doi: 10.1101/gad.468808. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

