Atorvastatin alters the expression of genes related to bile acid metabolism and circadian clock in livers of mice
- PMID: 28533986
- PMCID: PMC5438592
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.3348
Atorvastatin alters the expression of genes related to bile acid metabolism and circadian clock in livers of mice
Abstract
Aim: Atorvastatin is a HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor used for hyperlipidemia. Atorvastatin is generally safe but may induce cholestasis. The present study aimed to examine the effects of atorvastatin on hepatic gene expression related to bile acid metabolism and homeostasis, as well as the expression of circadian clock genes in livers of mice.
Methods: Adult male mice were given atorvastatin (10, 30, and 100 mg/kg, po) daily for 30 days, and blood biochemistry, histopathology, and gene expression were examined.
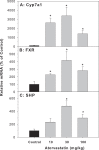
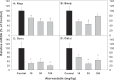
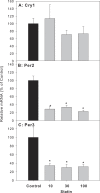
Results: Repeated administration of atorvastatin did not affect animal body weight gain or liver weights. Serum enzyme activities were in the normal range. Histologically, the high dose of atorvastatin produced scattered swollen hepatocytes, foci of feathery-like degeneration, together with increased expression of Egr-1 and metallothionein-1. Atorvastatin increased the expression of Cyp7a1 in the liver, along with FXR and SHP. In contract, atorvastatin decreased the expression of bile acid transporters Ntcp, Bsep, Ostα, and Ostβ. The most dramatic change was the 30-fold induction of Cyp7a1. Because Cyp7a1 is a circadian clock-controlled gene, we further examined the effect of atorvastatin on clock gene expression. Atorvastatin increased the expression of clock core master genes Bmal1 and Npas2, decreased the expression of clock feedback genes Per2, Per3, and the clock targeted genes Dbp and Tef, whereas it had no effect on Cry1 and Nr1d1 expression.
Conclusion: Repeated administration of atorvastatin affects bile acid metabolism and markedly increases the expression of the bile acid synthesis rate-limiting enzyme gene Cyp7a1, together with alterations in the expression of circadian clock genes.
Keywords: Atorvastatin; Bile acid transporters; Cholestasis; Clock gene expression; Cyp7a1; Mouse liver.
Conflict of interest statement
Jie Liu is an Academic Editor for PeerJ.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Differential patterns in the periodicity and dynamics of clock gene expression in mouse liver and stomach.Chronobiol Int. 2012 Dec;29(10):1300-11. doi: 10.3109/07420528.2012.728662. Epub 2012 Nov 6. Chronobiol Int. 2012. PMID: 23131081
-
Short-term circadian disruption impairs bile acid and lipid homeostasis in mice.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 Nov 1;1(6):664-677. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2015.08.003. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 26645046 Free PMC article.
-
Repeated manganese administration produced abnormal expression of circadian clock genes in the hypothalamus and liver of rats.Neurotoxicology. 2017 Sep;62:39-45. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2017.05.007. Epub 2017 May 13. Neurotoxicology. 2017. PMID: 28511934
-
The Tibetan medicine Zuotai influences clock gene expression in the liver of mice.PeerJ. 2016 Jan 26;4:e1632. doi: 10.7717/peerj.1632. eCollection 2016. PeerJ. 2016. PMID: 26855871 Free PMC article.
-
The influences of cholecystectomy on the circadian rhythms of bile acids as well as the enterohepatic transporters and enzymes systems in mice.Chronobiol Int. 2018 May;35(5):673-690. doi: 10.1080/07420528.2018.1426596. Epub 2018 Jan 30. Chronobiol Int. 2018. PMID: 29381405
Cited by
-
Personalized statin therapy: Targeting metabolic processes to modulate the therapeutic and adverse effects of statins.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 2;11(1):e41629. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41629. eCollection 2025 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 39866414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perturbation of the circadian clock and pathogenesis of NAFLD.Metabolism. 2020 Oct;111S:154337. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154337. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Metabolism. 2020. PMID: 32795560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Unhealthy Nutrition and Circadian Dysregulation in Pathophysiology of NAFLD.Front Clin Diabetes Healthc. 2021 Oct 12;2:691828. doi: 10.3389/fcdhc.2021.691828. eCollection 2021. Front Clin Diabetes Healthc. 2021. PMID: 36994336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA-Seq Profiling of Intestinal Expression of Xenobiotic Processing Genes in Germ-Free Mice.Drug Metab Dispos. 2017 Dec;45(12):1225-1238. doi: 10.1124/dmd.117.077313. Epub 2017 Sep 22. Drug Metab Dispos. 2017. PMID: 28939687 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Hepatic Metabolic Regulation by the Nuclear Factor Rev-erbɑ.Curr Drug Metab. 2024;25(1):2-12. doi: 10.2174/0113892002290055240212074758. Curr Drug Metab. 2024. PMID: 38409696 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

