Microglia: Housekeeper of the Central Nervous System
- PMID: 28534246
- PMCID: PMC11481884
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-017-0504-2
Microglia: Housekeeper of the Central Nervous System
Abstract
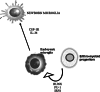
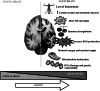
Microglia, of myeloid origin, play fundamental roles in the control of immune responses and the maintenance of central nervous system homeostasis. These cells, just like peripheral macrophages, may be activated into M1 pro-inflammatory or M2 anti-inflammatory phenotypes by appropriate stimuli. Microglia do not respond in isolation, but form part of complex networks of cells influencing each other. This review addresses the complex interaction of microglia with each cell type in the brain: neurons, astrocytes, cerebrovascular endothelial cells, and oligodendrocytes. We also highlight the participation of microglia in the maintenance of homeostasis in the brain, and their roles in the development and progression of age-related neurodegenerative disorders.
Keywords: Astrocytes; Brain aging; CNS keeper; Microglia activation; Neurons; Oligodendrocytes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest for this manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Ahluwalia A, Jones MK, Szabo S, Tarnawski AS (2014) Aging impairs transcriptional regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in human microvascular endothelial cells: implications for angiogenesis and cell survival. J Physiol Pharmacol 65:209–215 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

