Imaging of Cranial Nerves III, IV, VI in Congenital Cranial Dysinnervation Disorders
- PMID: 28534340
- PMCID: PMC5469921
- DOI: 10.3341/kjo.2017.0024
Imaging of Cranial Nerves III, IV, VI in Congenital Cranial Dysinnervation Disorders
Abstract
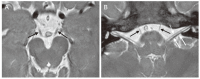
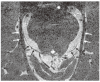
Congenital cranial dysinnervation disorders are a group of diseases caused by abnormal development of cranial nerve nuclei or their axonal connections, resulting in aberrant innervation of the ocular and facial musculature. Its diagnosis could be facilitated by the development of high resolution thin-section magnetic resonance imaging. The purpose of this review is to describe the method to visualize cranial nerves III, IV, and VI and to present the imaging findings of congenital cranial dysinnervation disorders including congenital oculomotor nerve palsy, congenital trochlear nerve palsy, Duane retraction syndrome, Möbius syndrome, congenital fibrosis of the extraocular muscles, synergistic divergence, and synergistic convergence.
Keywords: Congenital fibrosis of the extraocular muscles; Congenital trochlear nerve palsy; Duane retraction syndrome; Möbius syndrome; Oculomotor nerve palsy.
© 2017 The Korean Ophthalmological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Splitting of the extraocular horizontal rectus muscle in congenital cranial dysinnervation disorders.Am J Ophthalmol. 2009 Mar;147(3):550-556.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2008.09.015. Epub 2008 Nov 26. Am J Ophthalmol. 2009. PMID: 19038376
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Patients With Duane Retraction Syndrome.J Neuroophthalmol. 2024 Mar 1;44(1):101-106. doi: 10.1097/WNO.0000000000001909. Epub 2023 Sep 8. J Neuroophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 37682628 Free PMC article.
-
The congenital cranial dysinnervation disorders.Arch Dis Child. 2015 Jul;100(7):678-81. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2014-307035. Epub 2015 Jan 29. Arch Dis Child. 2015. PMID: 25633065 Review.
-
Imaging findings in congenital cranial dysinnervation disorders.Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2011 Dec;22(6):283-94. doi: 10.1097/RMR.0000000000000009. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2011. PMID: 24132067 Review.
-
MRI evaluation of cranial nerve abnormalities and extraocular muscle fibrosis in duane retraction syndrome and congenital extraocular muscle fibrosis.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2024 Aug;262(8):2633-2642. doi: 10.1007/s00417-024-06454-5. Epub 2024 Mar 26. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38530452
Cited by
-
On the Cranial Nerves.NeuroSci. 2023 Dec 28;5(1):8-38. doi: 10.3390/neurosci5010002. eCollection 2024 Mar. NeuroSci. 2023. PMID: 39483811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-resolution MRI demonstrates signal abnormalities of the 3rd cranial nerve in giant cell arteritis patients with 3rd cranial nerve impairment.Eur Radiol. 2021 Jul;31(7):4472-4480. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07595-x. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33439314
-
Complex strabismus: a case report of hypoplasia of the third cranial nerve with an unusual clinical presentation.Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2020 Sep-Oct;83(5):424-426. doi: 10.5935/0004-2749.20200083. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2020. PMID: 32785440 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroradiological and clinical features in ophthalmoplegia.Neuroradiology. 2019 Apr;61(4):365-387. doi: 10.1007/s00234-019-02183-3. Epub 2019 Feb 12. Neuroradiology. 2019. PMID: 30747268 Review.
-
Trochlear nerve agenesis in a patient with 18q22.2q23 deletion.Neurol Sci. 2024 Aug;45(8):4083-4085. doi: 10.1007/s10072-024-07554-0. Epub 2024 May 1. Neurol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38691274 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gutowski NJ, Bosley TM, Engle EC. 110th ENMC International Workshop: the congenital cranial dysinnervation disorders (CCDDs). Naarden, The Netherlands, 25–27 October, 2002. Neuromuscul Disord. 2003;13:573–578. - PubMed
-
- Kim JH, Hwang JM. Presence of the abducens nerve according to the type of Duane's retraction syndrome. Ophthalmology. 2005;112:109–113. - PubMed
-
- Ciftci E, Anik Y, Arslan A, et al. Driven equilibrium (drive) MR imaging of the cranial nerves V-VIII: comparison with the T2-weighted 3D TSE sequence. Eur J Radiol. 2004;51:234–240. - PubMed
-
- Kim JH, Hwang JM. Hypoplastic oculomotor nerve and absent abducens nerve in congenital fibrosis syndrome and synergistic divergence with magnetic resonance imaging. Ophthalmology. 2005;112:728–732. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical