Type IA topoisomerases can be "magicians" for both DNA and RNA in all domains of life
- PMID: 28534707
- PMCID: PMC5546716
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1330741
Type IA topoisomerases can be "magicians" for both DNA and RNA in all domains of life
Abstract
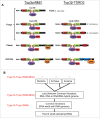
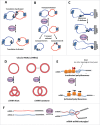
Topoisomerases solve critical topological problems in DNA metabolism and have long been regarded as the "magicians" of the DNA world. Here we present views from 2 of our recent studies indicating that Type IA topoisomerases from all domains of life often possess dual topoisomerase activities for both DNA and RNA. In animals, one of the 2 Type IA topoisomerases, Top3β, contains an RNA-binding domain, possesses RNA topoisomerase activity, binds mRNAs, interacts with mRNA-binding proteins, and associates with active mRNA translation machinery. The RNA-binding domain is required for Top3β to bind mRNAs and promote normal neurodevelopment. Top3β forms a highly conserved complex with Tudor-domain-containing 3 (TDRD3), a protein known to interact with translation factors, histones, RNA polymerase II, single stranded DNA and RNA. Top3β requires TDRD3 for its association with the mRNA translation machinery. We suggest that Type IA topoisomerases can be "magicians" for not only DNA, but also RNA; and they may solve topological problems for both nucleic acids in all domains of life. In animals, Top3β-TDRD3 is a dual-activity topoisomerase complex that can act on DNA to stimulate transcription, and on mRNA to promote translation.
Keywords: FMRP; TDRD3; Top3α; Top3β; polyribosomes; topoisomerase.
Figures


References
-
- Wang JC. Interaction between DNA and an Escherichia coli protein omega. J Mol Biol 1971; 55:523-33; PMID:4927945; https://doi.org/ 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90334-2 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang JC. Cellular roles of DNA topoisomerases: A molecular perspective. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2002; 3:430-40; PMID:12042765; https://doi.org/ 10.1038/nrm831 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pommier Y, Sun Y, Huang SN, Nitiss JL. Roles of eukaryotic topoisomerases in transcription, replication and genomic stability. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2016; 17(11):703-21; PMID:27649880; https://doi.org/ 10.1038/nrm.2016.111 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Forterre P, Gadelle D. Phylogenomics of DNA topoisomerases: Their origin and putative roles in the emergence of modern organisms. Nucleic Acids Res 2009; 37:679-92; PMID:19208647; https://doi.org/ 10.1093/nar/gkp032 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang JC. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem 1996; 65:635-92; PMID:8811192; https://doi.org/ 10.1146/annurev.bi.65.070196.003223 10.1146/annurev.biochem.65.1.635 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
