Effects of Ketogenic Diets on Cardiovascular Risk Factors: Evidence from Animal and Human Studies
- PMID: 28534852
- PMCID: PMC5452247
- DOI: 10.3390/nu9050517
Effects of Ketogenic Diets on Cardiovascular Risk Factors: Evidence from Animal and Human Studies
Abstract
The treatment of obesity and cardiovascular diseases is one of the most difficult and important challenges nowadays. Weight loss is frequently offered as a therapy and is aimed at improving some of the components of the metabolic syndrome. Among various diets, ketogenic diets, which are very low in carbohydrates and usually high in fats and/or proteins, have gained in popularity. Results regarding the impact of such diets on cardiovascular risk factors are controversial, both in animals and humans, but some improvements notably in obesity and type 2 diabetes have been described. Unfortunately, these effects seem to be limited in time. Moreover, these diets are not totally safe and can be associated with some adverse events. Notably, in rodents, development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and insulin resistance have been described. The aim of this review is to discuss the role of ketogenic diets on different cardiovascular risk factors in both animals and humans based on available evidence.
Keywords: NAFLD; cardiovascular risk factors; fibroblast growth factor (FGF21); insulin resistance; ketogenic diets; obesity; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
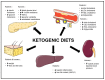
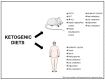
References
-
- Ng M., Fleming T., Robinson M., Thomson B., Graetz N., Margono C., Mullany E.C., Biryukov S., Abbafati C., Abera S.F., et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2014;384:766–781. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60460-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chalasani N., Younossi Z., Lavine J.E., Diehl A.M., Brunt E.M., Cusi K., Charlton M., Sanyal A.J. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guideline by the American Gastroenterological Association, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, and American College of Gastroenterology. Gastroenterology. 2012;142:1592–1609. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.04.001. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

