Identification of miR‑124a as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in non‑small cell lung cancer for chemotherapy
- PMID: 28534972
- PMCID: PMC5482144
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6595
Identification of miR‑124a as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in non‑small cell lung cancer for chemotherapy
Abstract
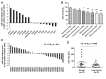
Previous studies have suggested that dysregulation of microRNA (miR) -124a is associated with various types of human cancer. However, there are few studies reporting the level of miR‑124a expression in non‑small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The present study investigated the association between miR‑124a and NSCLC by analyzing the differential expression of miR‑124a in NSCLC using the GEO database, as well as subsequently performing reverse transcription‑quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis on 160 NSCLC biopsies, 32 of which were paired with adjacent normal tissues. The results indicated that mir‑124a expression levels were decreased in NSCLC tumor biopsies compared with adjacent normal tissues. The overall survival (OS) in patients with a high expression of miR‑124a was prolonged relative to patients with low expression of miR‑124a. The expression levels of miR‑124a were associated with clinical characteristics, including lymph‑node metastasis, tumor differentiation, tumor node metastasis (TNM) stage and diameter. Frequently, lymph‑node metastasis, TNM stage, diameter and lack of chemotherapy have been associated with a worse prognosis in patients. In addition, the present study identified that high expression of miR‑124awith chemotherapy may increase OS. In conclusion, the current study demonstrated that miR‑124a was downregulated in NSCLC, and miR‑124a was a potential prognostic tumor biomarker response to chemotherapy.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Increased expression of microRNA-301a in nonsmall-cell lung cancer and its clinical significance.J Cancer Res Ther. 2016 Apr-Jun;12(2):693-8. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.146130. J Cancer Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27461635
-
MicroRNA-153 expression and prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jul 1;8(7):8671-5. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26339455 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulated MicroRNA 148b expression as predictive biomarker and its prognostic significance associated with clinicopathological features in non-small-cell lung cancer patients.Diagn Pathol. 2015 Sep 17;10:164. doi: 10.1186/s13000-015-0393-y. Diagn Pathol. 2015. Retraction in: Diagn Pathol. 2016 Nov 2;11(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s13000-016-0562-7. PMID: 26377406 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Strategies for clinical implementation of TNM-Immunoscore in resected nonsmall-cell lung cancer.Ann Oncol. 2016 Feb;27(2):225-32. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv560. Epub 2015 Nov 16. Ann Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26578726 Review.
-
Prognostic factors in NSCLC. Recent experiences.Lung Cancer. 1995 Apr;12 Suppl 1:S27-33. doi: 10.1016/0169-5002(95)00418-z. Lung Cancer. 1995. PMID: 7551931 Review.
Cited by
-
miR-30 Family Reduction Maintains Self-Renewal and Promotes Tumorigenesis in NSCLC-Initiating Cells by Targeting Oncogene TM4SF1.Mol Ther. 2018 Dec 5;26(12):2751-2765. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.09.006. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Mol Ther. 2018. PMID: 30301667 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of microRNA-124-5p sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells to treatment with 5-fluorouracil via AEG-1 regulation.Oncol Lett. 2021 Jan;21(1):5. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12266. Epub 2020 Nov 3. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33240411 Free PMC article.
-
Role of MicroRNA-124 as a Prognostic Factor in Multiple Neoplasms: A Meta-Analysis.Dis Markers. 2019 Nov 22;2019:1654780. doi: 10.1155/2019/1654780. eCollection 2019. Dis Markers. 2019. PMID: 31885731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-124a Regulates Extracellular Vesicle Release by Targeting GTPase Rabs in Lung Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 Aug 20;10:1454. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01454. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32974168 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of key candidate genes and miRNA‑mRNA target pairs in chronic lymphocytic leukemia by integrated bioinformatics analysis.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Jan;19(1):362-374. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9636. Epub 2018 Nov 9. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 30431072 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hamamoto J, Soejima K, Yoda S, Naoki K, Nakayama S, Satomi R, Terai H, Ikemura S, Sato T, Yasuda H, et al. Identification of microRNAs differentially expressed between lung squamous cell carcinoma and lung adenocarcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 2013;8:456–462. - PubMed
-
- Meng W, Ye Z, Cui R, Perry J, Dedousi-Huebner V, Huebner A, Wang Y, Li B, Volinia S, Nakanishi H, et al. MicroRNA-31 predicts the presence of lymph node metastases and survival in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19:5423–5433. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0320. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tiseo M, Bordi P, Bortesi B, Boni L, Boni C, Baldini E, Grossi F, Recchia F, Zanelli F, Fontanini G, et al. ERCC1/BRCA1 expression and gene polymorphisms as prognostic and predictive factors in advanced NSCLC treated with or without cisplatin. Br J Cancer. 2013;108:1695–1703. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.127. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

