Mms1 binds to G-rich regions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and influences replication and genome stability
- PMID: 28535251
- PMCID: PMC5570088
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkx467
Mms1 binds to G-rich regions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and influences replication and genome stability
Abstract
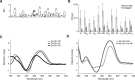
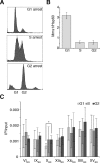
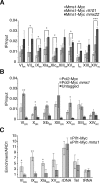
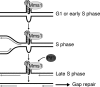
The regulation of replication is essential to preserve genome integrity. Mms1 is part of the E3 ubiquitin ligase complex that is linked to replication fork progression. By identifying Mms1 binding sites genome-wide in Saccharomyces cerevisiae we connected Mms1 function to genome integrity and replication fork progression at particular G-rich motifs. This motif can form G-quadruplex (G4) structures in vitro. G4 are stable DNA structures that are known to impede replication fork progression. In the absence of Mms1, genome stability is at risk at these G-rich/G4 regions as demonstrated by gross chromosomal rearrangement assays. Mms1 binds throughout the cell cycle to these G-rich/G4 regions and supports the binding of Pif1 DNA helicase. Based on these data we propose a mechanistic model in which Mms1 binds to specific G-rich/G4 motif located on the lagging strand template for DNA replication and supports Pif1 function, DNA replication and genome integrity.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

References
-
- Barbour L., Xiao W.. Regulation of alternative replication bypass pathways at stalled replication forks and its effects on genome stability: a yeast model. Mutat. Res. 2003; 532:137–155. - PubMed
-
- Luke B., Versini G., Jaquenoud M., Zaidi I.W., Kurz T., Pintard L., Pasero P., Peter M.. The cullin Rtt101p promotes replication fork progression through damaged DNA and natural pause sites. Curr. Biol.: CB. 2006; 16:786–792. - PubMed
-
- Duro E., Vaisica J.A., Brown G.W., Rouse J.. Budding yeast Mms22 and Mms1 regulate homologous recombination induced by replisome blockage. DNA Repair. 2008; 7:811–818. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

