A Brain-Region-Specific Neural Pathway Regulating Germinal Matrix Angiogenesis
- PMID: 28535372
- PMCID: PMC5492999
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.04.014
A Brain-Region-Specific Neural Pathway Regulating Germinal Matrix Angiogenesis
Abstract
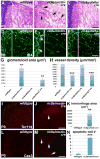
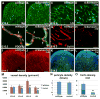
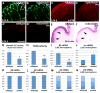
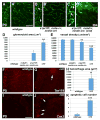
Intimate communication between neural and vascular cells is critical for normal brain development and function. Germinal matrix (GM), a key primordium for the brain reward circuitry, is unique among brain regions for its distinct pace of angiogenesis and selective vulnerability to hemorrhage during development. A major neonatal condition, GM hemorrhage can lead to cerebral palsy, hydrocephalus, and mental retardation. Here we identify a brain-region-specific neural progenitor-based signaling pathway dedicated to regulating GM vessel development. This pathway consists of cell-surface sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors, an intracellular cascade including Gα co-factor Ric8a and p38 MAPK, and target gene integrin β8, which in turn regulates vascular TGF-β signaling. These findings provide insights into region-specific specialization of neurovascular communication, with special implications for deciphering potent early-life endocrine, as well as potential gut microbiota impacts on brain reward circuitry. They also identify tissue-specific molecular targets for GM hemorrhage intervention.
Keywords: G-protein-coupled receptor; TGF-β; angiogenesis; basal ganglia; germinal matrix; integrin; neural stem cell; neurovascular signaling; radial glia; sphigosine-1-phosphate.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

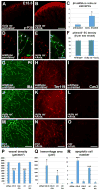
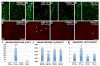
References
-
- Abe M, Harpel JG, Metz CN, Nunes I, Loskutoff DJ, Rifkin DB. An assay for transforming growth factor-beta using cells transfected with a plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 promoter-luciferase construct. Analytical biochemistry. 1994;216:276–284. - PubMed
-
- Allende ML, Yamashita T, Proia RL. G-protein-coupled receptor S1P1 acts within endothelial cells to regulate vascular maturation. Blood. 2003;102:3665–3667. - PubMed
-
- Armulik A, Genove G, Betsholtz C. Pericytes: developmental, physiological, and pathological perspectives, problems, and promises. Developmental cell. 2011;21:193–215. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

