Altered gene expression in early postnatal monoamine oxidase A knockout mice
- PMID: 28535982
- PMCID: PMC5531263
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2017.05.017
Altered gene expression in early postnatal monoamine oxidase A knockout mice
Abstract
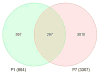
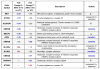
We reported previously that monoamine oxidase (MAO) A knockout (KO) mice show increased serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) levels and autistic-like behaviors characterized by repetitive behaviors, and anti-social behaviors. We showed that administration of the serotonin synthesis inhibitor para-chlorophenylalanine (pCPA) from post-natal day 1 (P1) through 7 (P7) in MAO A KO mice reduced the serotonin level to normal and reverses the repetitive behavior. These results suggested that the altered gene expression at P1 and P7 may be important for the autistic-like behaviors seen in MAO A KO mice and was studied here. In this study, Affymetrix mRNA array data for P1 and P7 MAO A KO mice were analyzed using Partek Genomics Suite and Ingenuity Pathways Analysis to identify genes differentially expressed versus wild-type and assess their functions and relationships. The number of significant differentially expressed genes (DEGs) varied with age: P1 (664) and P7 (3307) [false discovery rate (FDR) <0.05, fold-change (FC) >1.5 for autism-linked genes and >2.0 for functionally categorized genes]. Eight autism-linked genes were differentially expressed in P1 (upregulated: NLGN3, SLC6A2; down-regulated: HTR2C, MET, ADSL, MECP2, ALDH5A1, GRIN3B) while four autism-linked genes were differentially expressed at P7 (upregulated: HTR2B; downregulated: GRIN2D, GRIN2B, CHRNA4). Many other genes involved in neurodevelopment, apoptosis, neurotransmission, and cognitive function were differentially expressed at P7 in MAO A KO mice. This result suggests that modulation of these genes by the increased serotonin may lead to neurodevelopmental alteration in MAO A KO mice and results in autistic-like behaviors.
Keywords: Autism; Brain; Development; Monoamine oxidase; Serotonin.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Acquatella-Tran Van Ba I, Marchal S, Francois F, Shihol M, Lleres C, Michel B, Benyamin Y, Verdier JM, Trousse F, Marcihac A. Regenerating islet-derived 1α(Reg-1α) protein is new neuronal secreted factor that stimulates neurite outgrowth via exostosin Tumor-like 3(EXTL3) receptor. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:4726–4739. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ameis SH, Catani M. Altered white matter connectivity as a neural substrate for social impairment in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Cortex. 2015;62:158–181. - PubMed
-
- Bauman ML, Kemper TL. The neuropathology of the autism spectrum disorders: what have we learned? Novartis Found Symp. 2003;251:112–122. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

