A receptor-like protein acts as a specificity switch for the regulation of stomatal development
- PMID: 28536146
- PMCID: PMC5458759
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.297580.117
A receptor-like protein acts as a specificity switch for the regulation of stomatal development
Abstract
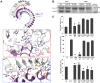
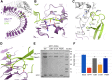
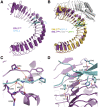
Stomata are microscopic openings that allow for the exchange of gases between plants and the environment. In Arabidopsis, stomatal patterning is specified by the ERECTA family (ERf) receptor kinases (RKs), the receptor-like protein (RLP) TOO MANY MOUTHS (TMM), and EPIDERMAL PATTERNING FACTOR (EPF) peptides. Here we show that TMM and ER or ER-LIKE1 (ERL1) form constitutive complexes, which recognize EPF1 and EPF2, but the single ERfs do not. TMM interaction with ERL1 creates a binding pocket for recognition of EPF1 and EPF2, indicating that the constitutive TMM-ERf complexes function as the receptors of EPF1 and EPF2. EPFL9 competes with EPF1 and EPF2 for binding to the ERf-TMM complex. EPFL4 and EPFL6, however, are recognized by the single ERfs without the requirement of TMM. In contrast to EPF1,2, the interaction of EPFL4,6 with an ERf is greatly reduced in the presence of TMM. Taken together, our data demonstrate that TMM dictates the specificity of ERfs for the perception of different EPFs, thus functioning as a specificity switch for the regulation of the activities of ERfs.
Keywords: biochemical interaction; peptide hormones; receptor kinases; receptor-like protein; stomatal development; structure.
© 2017 Lin et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Direct interaction of ligand-receptor pairs specifying stomatal patterning.Genes Dev. 2012 Jan 15;26(2):126-36. doi: 10.1101/gad.179895.111. Epub 2012 Jan 12. Genes Dev. 2012. PMID: 22241782 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of the peptides Stomagen, EPF1 and EPF2 on activation of MAP kinase MPK6 and the SPCH protein level.Plant Cell Physiol. 2013 Aug;54(8):1253-62. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pct076. Epub 2013 May 17. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23686240
-
Mix-and-match: ligand-receptor pairs in stomatal development and beyond.Trends Plant Sci. 2012 Dec;17(12):711-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2012.06.013. Epub 2012 Jul 21. Trends Plant Sci. 2012. PMID: 22819466 Review.
-
Autocrine regulation of stomatal differentiation potential by EPF1 and ERECTA-LIKE1 ligand-receptor signaling.Elife. 2017 Mar 7;6:e24102. doi: 10.7554/eLife.24102. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28266915 Free PMC article.
-
Take a deep breath: peptide signalling in stomatal patterning and differentiation.J Exp Bot. 2013 Dec;64(17):5243-51. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert246. Epub 2013 Aug 30. J Exp Bot. 2013. PMID: 23997204 Review.
Cited by
-
A receptor-like protein mediates plant immune responses to herbivore-associated molecular patterns.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Dec 8;117(49):31510-31518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2018415117. Epub 2020 Nov 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 33229576 Free PMC article.
-
Competitive binding of small antagonistic peptides to the OsER1 receptor optimizes rice panicle architecture.Plant Commun. 2025 Mar 10;6(3):101204. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2024.101204. Epub 2024 Dec 6. Plant Commun. 2025. PMID: 39645583 Free PMC article.
-
Cell identity specification in plants: lessons from flower development.J Exp Bot. 2021 May 28;72(12):4202-4217. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erab110. J Exp Bot. 2021. PMID: 33865238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimization of rice panicle architecture by specifically suppressing ligand-receptor pairs.Nat Commun. 2023 Mar 24;14(1):1640. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37326-x. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36964129 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling by the EPFL-ERECTA family coordinates female germline specification through the BZR1 family in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2023 Apr 20;35(5):1455-1473. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koad032. Plant Cell. 2023. PMID: 36748257 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrash EB, Bergmann DC. 2010. Regional specification of stomatal production by the putative ligand CHALLAH. Development 137: 447–455. - PubMed
-
- Adams PD, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Hung LW, Ioerger TR, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Read RJ, Sacchettini JC, Sauter NK, Terwilliger TC. 2002. PHENIX: building new software for automated crystallographic structure determination. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 58: 1948–1954. - PubMed
-
- Clough SJ, Bent AF. 1998. Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16: 735–743. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
