Vascular endothelial growth factor modified macrophages transdifferentiate into endothelial-like cells and decrease foam cell formation
- PMID: 28536311
- PMCID: PMC5479018
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20170002
Vascular endothelial growth factor modified macrophages transdifferentiate into endothelial-like cells and decrease foam cell formation
Abstract
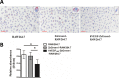
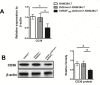
Macrophages are largely involved in the whole process of atherosclerosis from an initiation lesion to an advanced lesion. Endothelial disruption is the initial step and macrophage-derived foam cells are the hallmark of atherosclerosis. Promotion of vascular integrity and inhibition of foam cell formation are two important strategies for preventing atherosclerosis. How can we inhibit even the reverse negative role of macrophages in atherosclerosis? The present study was performed to investigate if overexpressing endogenous human vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) could facilitate transdifferentiation of macrophages into endothelial-like cells (ELCs) and inhibit foam cell formation. We demonstrated that VEGF-modified macrophages which stably overexpressed human VEGF (hVEGF165) displayed a high capability to alter their phenotype and function into ELCs in vitro Exogenous VEGF could not replace endogenous VEGF to induce the transdifferentiation of macrophages into ELCs in vitro We further showed that VEGF-modified macrophages significantly decreased cytoplasmic lipid accumulation after treatment with oxidized LDL (ox-LDL). Moreover, down-regulation of CD36 expression in these cells was probably one of the mechanisms of reduction in foam cell formation. Our results provided the in vitro proof of VEGF-modified macrophages as atheroprotective therapeutic cells by both promotion of vascular repair and inhibition of foam cell formation.
Keywords: endothelial-like cells; foam cell; macrophages; vascular endothelial growth factor.
© 2017 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures



Similar articles
-
TRPV4 calcium-permeable channel is a novel regulator of oxidized LDL-induced macrophage foam cell formation.Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 Sep;110:142-150. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.06.004. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28602913
-
Inhibitions of vascular endothelial growth factor expression and foam cell formation by EGb 761, a special extract of Ginkgo biloba, in oxidatively modified low-density lipoprotein-induced human THP-1 monocytes cells.Phytomedicine. 2009 Mar;16(2-3):138-45. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2008.11.003. Epub 2009 Jan 8. Phytomedicine. 2009. PMID: 19135347
-
Postprandial lipoproteins and the molecular regulation of vascular homeostasis.Prog Lipid Res. 2013 Oct;52(4):446-64. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jun 15. Prog Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23774609 Review.
-
Kaempferol suppresses lipid accumulation in macrophages through the downregulation of cluster of differentiation 36 and the upregulation of scavenger receptor class B type I and ATP-binding cassette transporters A1 and G1.Int J Mol Med. 2013 Feb;31(2):331-8. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2012.1204. Epub 2012 Dec 5. Int J Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23232972
-
Smooth muscle cell phenotypic switch: implications for foam cell formation.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2014 Oct;25(5):374-9. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000113. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2014. PMID: 25110900 Review.
Cited by
-
Transition of Macrophages to Fibroblast-Like Cells in Healing Myocardial Infarction.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Dec 24;74(25):3124-3135. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.10.036. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31856969 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of crucial genes that induce coronary atherosclerosis through endothelial cell dysfunction in AMI-identifying hub genes by WGCNA.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Nov 15;14(11):8166-8174. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 36505315 Free PMC article.
-
Chemically Engineered Immune Cell-Derived Microrobots and Biomimetic Nanoparticles: Emerging Biodiagnostic and Therapeutic Tools.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Mar 1;8(8):2002499. doi: 10.1002/advs.202002499. eCollection 2021 Apr. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 33898169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of legumain in metabolic dysfunction, diagnosis, and prognosis of patients with atherosclerosis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jul 19;103(29):e38896. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038896. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39029045 Free PMC article.
-
The Crosstalk Between Endothelial Cells, Smooth Muscle Cells, and Macrophages in Atherosclerosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 10;26(4):1457. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041457. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40003923 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Thompson R.C., Allam A.H., Lombardi G.P., Wann L.S., Sutherland M.L. et al. (2013) Atherosclerosis across 4000 years of human history: the Horus study of four ancient populations. Lancet 381, 1211–1222 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

