Aptamer Technology: Adjunct Therapy for Malaria
- PMID: 28536344
- PMCID: PMC5423489
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines5010001
Aptamer Technology: Adjunct Therapy for Malaria
Abstract
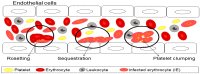
Malaria is a life-threatening parasitic infection occurring in the endemic areas, primarily in children under the age of five, pregnant women, and patients with human immunodeficiency virus and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV)/(AIDS) as well as non-immune individuals. The cytoadherence of infected erythrocytes (IEs) to the host endothelial surface receptor is a known factor that contributes to the increased prevalence of severe malaria cases due to the accumulation of IEs, mainly in the brain and other vital organs. Therefore, further study is needed to discover a new potential anti-adhesive drug to treat severe malaria thus reducing its mortality rate. In this review, we discuss how the aptamer technology could be applied in the development of a new adjunct therapy for current malaria treatment.
Keywords: Plasmodium falciparum; adjunct therapy; aptamer; cytoadherence; malaria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) World Malaria Report. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2015. p. 280.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

