In vitro chondrogenesis of Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells in hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels
- PMID: 28536614
- PMCID: PMC5415830
- DOI: 10.1186/s11658-016-0016-y
In vitro chondrogenesis of Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells in hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels
Abstract
Background: In this study, we evaluated the usefulness of two commercially available hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels, HyStem and HyStem-C, for the cultivation of Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells (WJ-MSCs) and their differentiation towards chondrocytes.
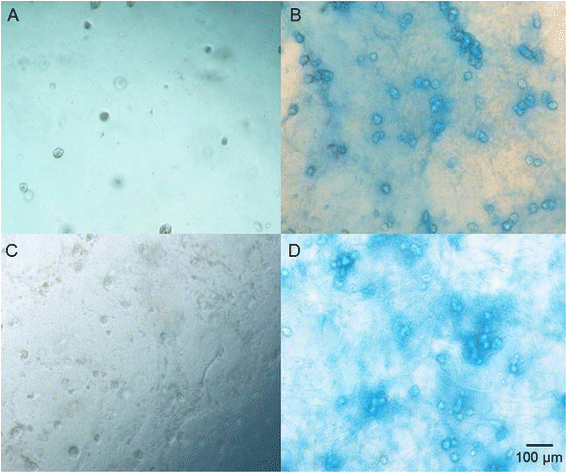
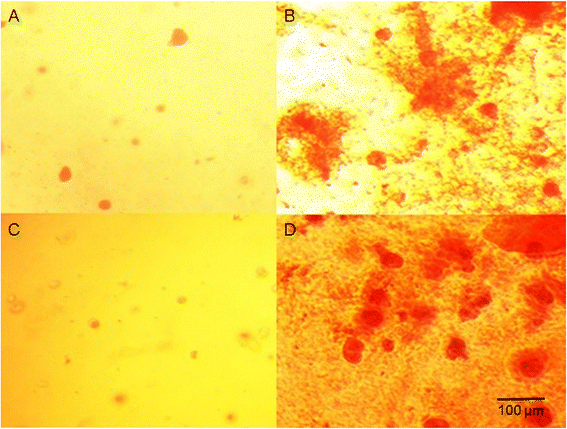
Methods: The WJ-MSCs were isolated from umbilical cord Wharton's jelly using the explant method and their immunophenotype was evaluated via flow cytometry analysis. According to the criteria established by the International Society for Cellular Therapy, they were true MSCs. We assessed the ability of the WJ-MSCs and chondrocytes to grow in three-dimensional hydrogels and their metabolic activity. Chondrogenesis of WJ-MSCs in the hydrogels was determined using alcian blue and safranin O staining and real-time PCR evaluation of gene expression in the extracellular matrixes: collagen type I, II, III and aggrecan.
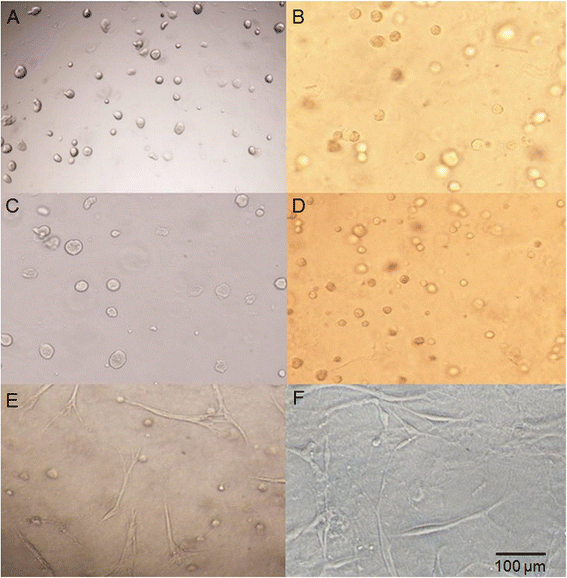
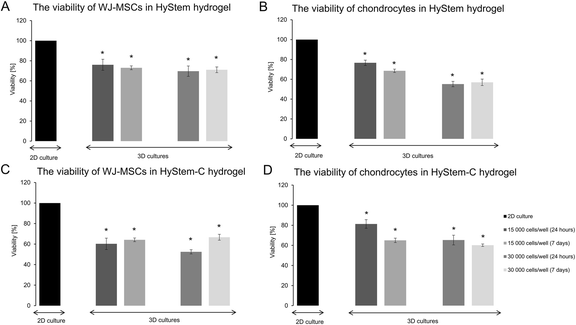
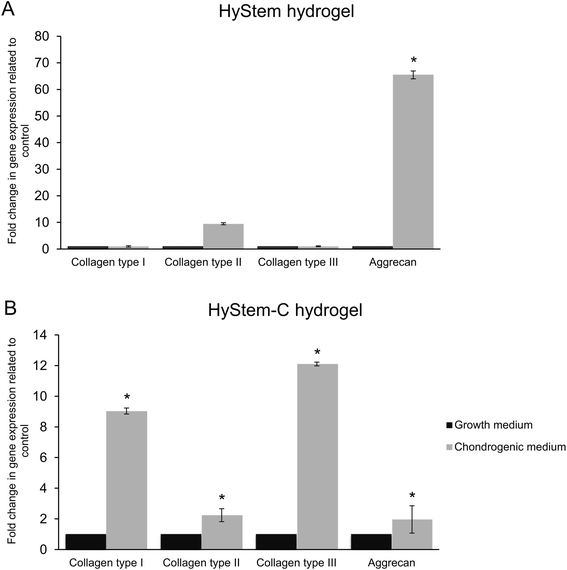
Results: Chondrocytes and WJ-MSCs cultured in the HyStem and HyStem-C hydrogels adopted spherical shapes, which are characteristic for encapsulated cells. The average viability of the WJ-MSCs and chondrocytes in the HyStem hydrogels was approximately 67 % when compared with the viability in 2D culture. Alcian blue and safranin O staining revealed intensive production of proteoglycans by the cells in the HyStem hydrogels. Increased expression of collagen type II and aggrecan in the WJ-MSCs cultured in the HyStem hydrogel in the presence of chondrogenic medium showed that under these conditions, the cells have a high capacity to differentiate towards chondrocytes. The relatively high viability of WJ-MSCs and chondrocytes in both HyStem hydrogels suggests the possibility of their use for chondrogenesis.
Conlusions: The results indicate that WJ-MSCs have some degree of chondrogenic potential in HyStem and HyStem-C hydrogels, showing promise for the engineering of damaged articular cartilage.
Keywords: Chondrocytes; Chondrogenesis; HyStem; HyStem-C; Hydrogels; WJ-MSCs.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

