Posttranscriptional and transcriptional regulation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase during hypoxia: the role of microRNAs
- PMID: 28536619
- PMCID: PMC5415778
- DOI: 10.1186/s11658-016-0017-x
Posttranscriptional and transcriptional regulation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase during hypoxia: the role of microRNAs
Abstract
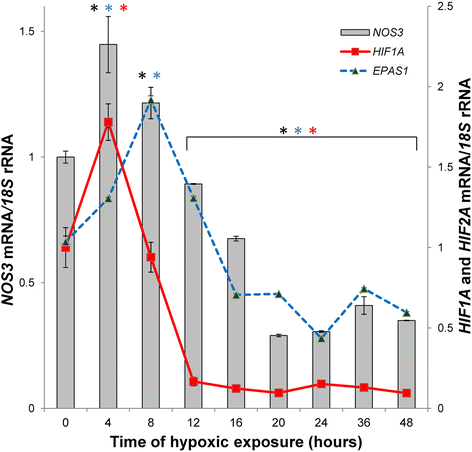
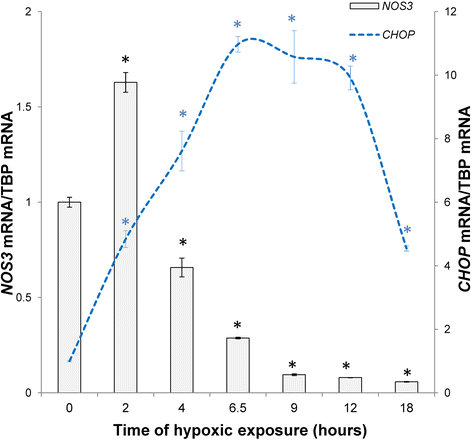
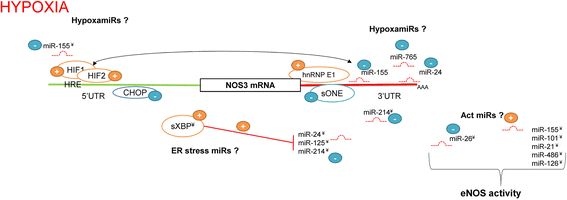
Understanding the cellular pathways that regulate endothelial nitric oxide (eNOS, NOS3) expression and consequently nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability during hypoxia is a necessary aspect in the development of novel treatments for cardiovascular disorders. eNOS expression and eNOS-dependent NO cellular signaling during hypoxia promote an equilibrium of transcriptional and posttranscriptional molecular mechanisms that belong to both proapoptotic and survival pathways. Furthermore, NO bioavailability results not only from eNOS levels, but also relies on the presence of eNOS substrate and cofactors, the phosphorylation status of eNOS, and the presence of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that can inactivate eNOS. Since both NOS3 levels and these signaling pathways can also be a subject of posttranscriptional modulation by microRNAs (miRNAs), this class of short noncoding RNAs contribute another level of regulation for NO bioavailability. As miRNA antagomirs or specific target protectors could be used in therapeutic approaches to regulate NO levels, either by changing NOS3 mRNA stability or through factors governing eNOS activity, it is critical to understand their role in governing eNOS activity during hypoxa. In contrast to a large number of miRNAs reported to the change eNOS expression during hypoxia, only a few miRNAs modulate eNOS activity. Furthermore, impaired miRNA biogenesis leads to NOS3 mRNA stabilization under hypoxia. Here we discuss the recent studies that define miRNAs' role in maintaining endothelial NO bioavailability emphasizing those miRNAs that directly modulate NOS3 expression or eNOS activity.
Keywords: ER stress; Hypoxia; NO bioavailability; NOS3; Nitric oxide; eNOS; miRNA; sONE.
Figures
References
-
- Channon KM, Guzik TJ. Mechanisms of superoxide production in human blood vessels: relationship to endothelial dysfunction, clinical and genetic risk factors. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2002;53:515–524. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

