The Characteristics Of Human Bone-Derived Cells (HBDCS) during osteogenesis in vitro
- PMID: 28536628
- PMCID: PMC5415846
- DOI: 10.1186/s11658-016-0027-8
The Characteristics Of Human Bone-Derived Cells (HBDCS) during osteogenesis in vitro
Abstract
Background: The primary human bone-derived cell culture technique is used as a model to study human osteogenesis. Compared to cell line cultures, primary osteoprogenitor and osteoblast cultures provide more complex information about osteogenesis, bone remodeling and regeneration than cell line cultures.
Methods: In this study, we isolated human bone-derived cells (HBDCs) and promoted their differentiation into osteoblasts. The following parameters were evaluated: cell number and viability, total protein expression, alkaline phosphatase activity, collagenous matrix production and osteogenic genes expression, i.e., gene coding for type I collagen and alkaline phosphatase.
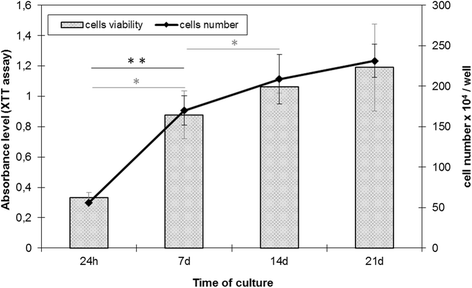
Results: It was proved the results show that HBDCs intensively proliferate during the first 7 days of culture followed by differentiation accompanied by an increase in alkaline phosphatase activity. Moreover, it was observed that during the differentiation of HBDCs, the expression of integrin β1 increased.
Conclusions: The process was also accompanied by changes in cell shape and rearrangement of the actin cytoskeleton and focal contacts containing FAK and the integrin β1 subunit. We suggest that the β1 integrin subunit may be a suitable new target in studies of the differentiation of primary human osteoblasts in culture.
Keywords: Human bone-derived cells; Integrins; Osteoblast differentiation; Osteogenesis in vitro; Osteogenic markers; Primary osteoblasts.
Figures





References
-
- Owen TA, Aronow M, Shalhoub V, Barone LM, Wilming L, Tassinari MS, Kennedy MB, Pockwinse S, Lian JB, Stein GS. Progressive development of the rat osteoblast phenotype in vitro: reciprocal relationships in expression of genes associated with osteoblast proliferation and differentiation during formation of the bone extracellular matrix. J Cell Physiol. 1990;143:420–30. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041430304. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Igarashi M, Kamiya N, Hasegawa M, Kasuya T, Takahashi T, Takagi M. Inductive effects of dexamethasone on the gene expression of Cbfa1, Osterix and bone matrix proteins during differentiation of cultured primary rat osteoblasts. J Mol Histol. 2004;35:3–10. doi: 10.1023/B:HIJO.0000020883.33256.fe. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

