Recent advances in capsule-based dry powder inhaler technology
- PMID: 28536654
- PMCID: PMC5439154
- DOI: 10.1186/s40248-017-0092-5
Recent advances in capsule-based dry powder inhaler technology
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: Recent advances in capsule-based dry powder inhaler technology.Multidiscip Respir Med. 2017 Jun 23;12:19. doi: 10.1186/s40248-017-0100-9. eCollection 2017. Multidiscip Respir Med. 2017. PMID: 28652914 Free PMC article.
Abstract
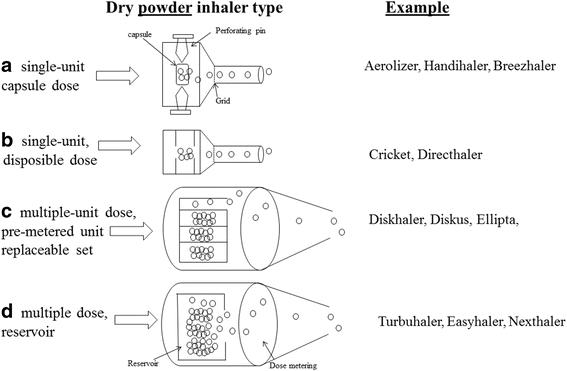
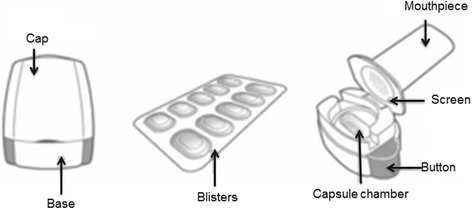
Pulmonary drug delivery is currently the focus of accelerated research and development because of the potential to produce maximum therapeutic benefit to patients by directly targeting drug to the site of pathology in the lungs. Among the available delivery options, the dry powder inhaler (DPI) is the preferred device for the treatment of an increasingly diverse range of diseases. However, because drug delivery from a DPI involves a complex interaction between the device and the patient, the engineering development of this medical technology is proving to be a great challenge. Development of DPI systems that target the delivery of fine drug particles to the deeper airways in the lungs using a combination of improved drug formulations and enhanced delivery device technologies means that each of these factors contributes to overall performance of the aerosol system. There are a large range of devices that are currently available, or under development, for clinical use, however no individual device shows superior clinical efficacy. A major concern that is very relevant in day-to-day clinical practice is the inter- and intra-patient variability of the drug dosage delivered to the deep lungs from the inhalation devices, where the extent of variability depends on the drug formulation, the device design, and the patient's inhalation profile. This variability may result in under-dosing of drug to the patient and potential loss of pharmacological efficacy. This article reviews recent advances in capsule-based DPI technology and the introduction of the 'disposable' DPI device.
Keywords: Asthma; Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; Drug delivery; Dry powder inhalers; Technology assessment.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Developing an efficient and reliable dry powder inhaler for pulmonary drug delivery--a review for multidisciplinary researchers.Med Eng Phys. 2012 May;34(4):409-27. doi: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2011.12.025. Epub 2012 Jan 23. Med Eng Phys. 2012. PMID: 22277307 Review.
-
Dry powder inhalers in COPD, lung inflammation and pulmonary infections.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015 Jun;12(6):947-62. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2015.977783. Epub 2014 Nov 12. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015. PMID: 25388926 Review.
-
The clinical relevance of dry powder inhaler performance for drug delivery.Respir Med. 2014 Aug;108(8):1195-203. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2014.05.009. Epub 2014 May 24. Respir Med. 2014. PMID: 24929253
-
Computationally efficient analysis of particle transport and deposition in a human whole-lung-airway model. Part II: Dry powder inhaler application.Comput Biol Med. 2017 May 1;84:247-253. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2016.10.025. Epub 2016 Nov 3. Comput Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 27836120
-
Development of a dry powder inhaler, the Ultrahaler, containing triamcinolone acetonide using in vitro-in vivo relationships.Am J Ther. 2006 Jan-Feb;13(1):32-42. doi: 10.1097/01.mjt.0000145357.13410.a9. Am J Ther. 2006. PMID: 16428920 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Dry Powder Inhalers in the Digitalization Era: Current Status and Future Perspectives.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Sep 12;13(9):1455. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13091455. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34575530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improved Physical Stability and Aerosolization of Inhalable Amorphous Ciprofloxacin Powder Formulations by Incorporating Synergistic Colistin.Mol Pharm. 2018 Sep 4;15(9):4004-4020. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00445. Epub 2018 Aug 3. Mol Pharm. 2018. PMID: 30028947 Free PMC article.
-
Patients with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can generate sufficient inspiratory flows via Easyhaler® dry powder inhaler: a pooled analysis of two randomized controlled trials.J Thorac Dis. 2021 Feb;13(2):621-631. doi: 10.21037/jtd-20-2112. J Thorac Dis. 2021. PMID: 33717535 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing bioavailability of natural extracts for nutritional applications through dry powder inhalers (DPI) spray drying: technological advancements and future directions.Front Nutr. 2023 Jul 5;10:1190912. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1190912. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37476406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the Physico-mechanical Properties and Electrostatic Charging Behavior of Different Capsule Types for Inhalation Under Distinct Environmental Conditions.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2020 May 12;21(4):128. doi: 10.1208/s12249-020-01676-2. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2020. PMID: 32399597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for AsthmaManagement and. Prevention, 2016. Available from: www.ginasthma.
-
- Crompton GK. Problems patients have using pressurised aerosol inhalers. Eur J Respir Dis. 1982;119:101–104. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

