CPS1 maintains pyrimidine pools and DNA synthesis in KRAS/LKB1-mutant lung cancer cells
- PMID: 28538732
- PMCID: PMC5472349
- DOI: 10.1038/nature22359
CPS1 maintains pyrimidine pools and DNA synthesis in KRAS/LKB1-mutant lung cancer cells
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: CPS1 maintains pyrimidine pools and DNA synthesis in KRAS/LKB1-mutant lung cancer cells.Nature. 2019 May;569(7756):E4. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1133-3. Nature. 2019. PMID: 31043737
Abstract
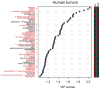
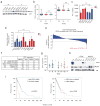
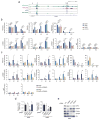
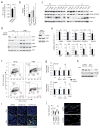
Metabolic reprogramming by oncogenic signals promotes cancer initiation and progression. The oncogene KRAS and tumour suppressor STK11, which encodes the kinase LKB1, regulate metabolism and are frequently mutated in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Concurrent occurrence of oncogenic KRAS and loss of LKB1 (KL) in cells specifies aggressive oncological behaviour. Here we show that human KL cells and tumours share metabolomic signatures of perturbed nitrogen handling. KL cells express the urea cycle enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthetase-1 (CPS1), which produces carbamoyl phosphate in the mitochondria from ammonia and bicarbonate, initiating nitrogen disposal. Transcription of CPS1 is suppressed by LKB1 through AMPK, and CPS1 expression correlates inversely with LKB1 in human NSCLC. Silencing CPS1 in KL cells induces cell death and reduces tumour growth. Notably, cell death results from pyrimidine depletion rather than ammonia toxicity, as CPS1 enables an unconventional pathway of nitrogen flow from ammonia into pyrimidines. CPS1 loss reduces the pyrimidine to purine ratio, compromises S-phase progression and induces DNA-polymerase stalling and DNA damage. Exogenous pyrimidines reverse DNA damage and rescue growth. The data indicate that the KL oncological genotype imposes a metabolic vulnerability related to a dependence on a cross-compartmental pathway of pyrimidine metabolism in an aggressive subset of NSCLC.
Figures







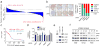

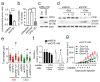
References
-
- Liu Y, et al. Metabolic and functional genomic studies identify deoxythymidylate kinase as a target in LKB1-mutant lung cancer. Cancer discovery. 2013;3:870–879. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.cd-13-0015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

