Lymphatic endothelial S1P promotes mitochondrial function and survival in naive T cells
- PMID: 28538737
- PMCID: PMC5683179
- DOI: 10.1038/nature22352
Lymphatic endothelial S1P promotes mitochondrial function and survival in naive T cells
Abstract
Effective adaptive immune responses require a large repertoire of naive T cells that migrate throughout the body, rapidly identifying almost any foreign peptide. Because the production of T cells declines with age, naive T cells must be long-lived. However, it remains unclear how naive T cells survive for years while constantly travelling. The chemoattractant sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) guides T cell circulation among secondary lymphoid organs, including spleen, lymph nodes and Peyer's patches, where T cells search for antigens. The concentration of S1P is higher in circulatory fluids than in lymphoid organs, and the S1P1 receptor (S1P1R) directs the exit of T cells from the spleen into blood, and from lymph nodes and Peyer's patches into lymph. Here we show that S1P is essential not only for the circulation of naive T cells, but also for their survival. Using transgenic mouse models, we demonstrate that lymphatic endothelial cells support the survival of T cells by secreting S1P via the transporter SPNS2, that this S1P signals through S1P1R on T cells, and that the requirement for S1P1R is independent of the established role of the receptor in guiding exit from lymph nodes. S1P signalling maintains the mitochondrial content of naive T cells, providing cells with the energy to continue their constant migration. The S1P signalling pathway is being targeted therapeutically to inhibit autoreactive T cell trafficking, and these findings suggest that it may be possible simultaneously to target autoreactive or malignant cell survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures





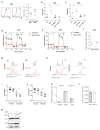


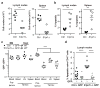
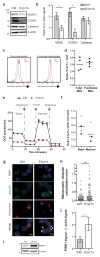
Comment in
-
Sphingosine-1-Phosphate as the Lymphocyte's Ticket to Ride and Survive.Dev Cell. 2017 Jun 19;41(6):576-578. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.06.006. Dev Cell. 2017. PMID: 28633013
-
T cells: Staying alive with S1P.Nat Rev Immunol. 2017 Jun 27;17(7):404-405. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.73. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28652598 No abstract available.
-
S1P: the elixir of life for naive T cells.Cell Mol Immunol. 2018 Jul;15(7):657-659. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2017.110. Epub 2017 Oct 30. Cell Mol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29082923 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Jenkins MK, Chu HH, McLachlan JB, Moon JJ. On the composition of the preimmune repertoire of T cells specific for Peptide-major histocompatibility complex ligands. Annual review of immunology. 2010;28:275–294. - PubMed
-
- Boehm T, Swann JB. Thymus involution and regeneration: two sides of the same coin? Nature reviews. Immunology. 2013;13:831–838. - PubMed
-
- Cyster JG, Schwab SR. Sphingosine-1-phosphate and lymphocyte egress from lymphoid organs. Annual review of immunology. 2012;30:69–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI123308/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI124129/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI085166/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007308/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA194547/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA202025/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI043542/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI100853/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA206005/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA196521/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL089934/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

