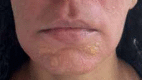
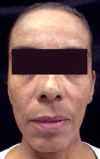
Tretinoin peeling: when a reaction is greater than expected
- PMID: 28538908
- PMCID: PMC5429134
- DOI: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20176728
Tretinoin peeling: when a reaction is greater than expected
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests: None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High-strength tretinoin: a method for rapid retinization of facial skin.J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998 Aug;39(2 Pt 3):S93-7. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(98)70454-2. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998. PMID: 9703133 Clinical Trial. No abstract available.
-
Efficacy of combination of glycolic acid peeling with topical regimen in treatment of melasma.J Drugs Dermatol. 2013 Oct;12(10):1149-53. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013. PMID: 24085051 Clinical Trial.
-
Physical signs for the general dental practitioner. Case 56. A chemical facial peel using Alphahydroxy acid (AHA).Dent Update. 2008 Jul-Aug;35(6):428. Dent Update. 2008. PMID: 18717108 No abstract available.
-
Complications of chemical face peeling: prevention and management.Facial Plast Surg. 1995 Jan;11(1):39-46. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1064515. Facial Plast Surg. 1995. PMID: 8995900 Review. No abstract available.
-
[Chemical peeling in dermatology].Hautarzt. 2019 Jul;70(7):535-546. doi: 10.1007/s00105-019-4438-0. Hautarzt. 2019. PMID: 31197390 Review. German.
References
-
- Cucé LC, Bertino MC, Scattone L, Birkenhauer MC. Tretinoin peeling. Dermatol Surg. 2001;27:12–14. - PubMed
-
- Magalhães GM, Borges MFM, Queiroz ARC, Capp AA, Pedrosa SV, Diniz MS. Estudo duplo-cego e randomizado do peeling de ácido retinóico a 5% e 10% no tratamento do melasma: avaliação clínica e impacto na qualidade de vida. Surg Cosmet Dermatol. 2011;3:17–22.
-
- Kligman DE, Sadiq I, Pagnoni A, Stoudemayer T, Kligman AM. High-strength tretinoin: a method for rapid retinization of facial skin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39:S93–S97. - PubMed
-
- Tosti A, Guerra L, Morelli R, Piraccini BM. Contact dermatitis due to topical retinoic acid. Contact Dermatitis. 1992;26:276–277. - PubMed
-
- Nordqvist BC, Mehr K. Allergic contact dermatitis to retinoic acid. Contact Dermatitis. 1977;3:55–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources