Effect of Helix aspersa extract on TNFα, NF-κB and some tumor suppressor genes in breast cancer cell line Hs578T
- PMID: 28539722
- PMCID: PMC5421427
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-1296.204618
Effect of Helix aspersa extract on TNFα, NF-κB and some tumor suppressor genes in breast cancer cell line Hs578T
Abstract
Background: The garden snail, Helix aspersa, is a big land snail widely found in the Mediterranean countries. It is one of the most consumed species and widely used in zootherapy.
Objective: The present study was carried out to investigate for the first time the first time the antitumor activity of an aqueous extract from Helix aspersa.
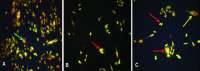
Materials and methods: The effect of H. aspersa extract was studied on a triple negative breast cancer cell line Hs578T. Firstly, the morphological changes and the mode of cell death induced by the extract have been evaluated by microscopy and acridine orange/ethidium bromide staining. The effect of the extract at dilution 0.1% and 1% was then tested on some genes, regulators of cell death and proliferation like tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα), NF- κB, and the tumor suppressor genes P53 and PTEN.
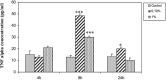
Results: Data demonstrate that the extract induces necrosis in tumor cells. It enhances significantly the expression of TNFα; mRNA levels were 20 and 10 times more important in treated cells compared to nontreated cells. NF-κB and PTEN were inhibited with the dilution 1% after 8 and 24 hours of treatment. P53 expression was further inhibited but only with the highest dose, after 4, 8, and 24 hours.
Conclusion: Our results show that H. aspersa extract has an antitumor activity against Hs578T cells; it is a potent stimulator for TNFα and a good inhibitor for NF-κB. Abbreviations used: AO: acridine orange; Bcl-2: B cell lymphoma 2. cDNA: complementary DNA; ELISA: enzyme linked immunosorbent assay; EB: ethidium bromide; IC50: the half maximal inhibitory concentration; mRNA: messenger RNA. MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-κB: nuclearfactorkappa B; PBS: phosphate buffered saline. PI3K: phospho-inositol 3 kinase; PTEN: phosphatase and tensin homolog; ROS: reactive oxygen species. RT-PCR: reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; TNFα: tumor necrosis factor alpha. TNFR1: TNF receptor-1; TP53: tumor protein 53.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Helix aspersa; NF-Kβ; TNFα; necrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Amin A, Moussa M. Merits of anti cancer plants from the Arabian Gulf region. Cancer therapy. 2007;5:55–66.
-
- Cagiltay F, Erkan N, Tosun D, Selcuk A. Amino acid, Fatty acid, vitamin and mineral contents of Edible garden snail (Helix aspersa) Journal of Fisheries Sciences. 2011;5:354–63.
-
- Ozogul y, Ozygul F, Olgunoglu A. Fatty acid profile and mineral content of wild snail Helix pomatia from the region of south of the turkey. Eur. Food. Res. Technol. 2004;221:547–49.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
