Review of effects of anti-VEGF treatment on refractive error
- PMID: 28539808
- PMCID: PMC5398745
- DOI: 10.2147/EB.S99306
Review of effects of anti-VEGF treatment on refractive error
Abstract
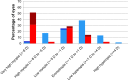
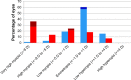
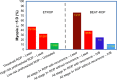
To examine the effect of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) agents on refractive error in the setting of retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) through a review of the literature, a PubMed search was performed of appropriate search terms, and the results of all relevant studies were extracted and compiled. Eleven relevant articles were identified in the literature, totaling 466 eyes, treated with varied anti-VEGF agents (bevacizumab, ranibizumab, and aflibercept) with mean spherical equivalent refractions ranging from +0.75 D to -3.57 D, with prevalence of high myopia ranging from 0 to 35%. Anti-VEGF monotherapy for ROP leads to low levels of myopia, and there may be a differential effect of specific anti-VEGF agents utilized on refractive outcomes.
Keywords: ROP; aflibercept; bevacizumab; myopia; ranibizumab; refraction; retinopathy of prematurity.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interests in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Geloneck MM, Chuang AZ, Clark WL, et al. Refractive outcomes following bevacizumab monotherapy compared with conventional laser treatment: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2014;132(11):1327–1333. - PubMed
-
- Quinn GE, Dobson V, Kivlin J, et al. Prevalence of myopia between 3 months and 5½ years in preterm infants with and without retinopathy of prematurity. Ophthalmology. 1998;105(7):1292–1300. - PubMed
-
- Quinn GE, Dobson V, Davitt BV, et al. Progression of myopia and high myopia in the Early Treatment for Retinopathy of Prematurity study: findings to 3 years of age. Ophthalmology. 2008;115(6):1058–1064.e1. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

