Increased expression of thyroid hormone responsive protein (THRSP) is the result but not the cause of higher intramuscular fat content in cattle
- PMID: 28539828
- PMCID: PMC5441172
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.18775
Increased expression of thyroid hormone responsive protein (THRSP) is the result but not the cause of higher intramuscular fat content in cattle
Abstract
Thyroid hormone responsive protein (THRSP) is known to be involved in lipogenic processes in rodents. In cattle, THRSP could be a potential molecular marker for intramuscular fat (IMF) deposition since mRNA abundance was frequently found to be increased in skeletal muscle with high IMF content compared to those with low IMF. The aim of this study was to elucidate the background of this differential expression and to evaluate the role of THRSP as candidate for increased IMF content in cattle. By combination of mRNA and protein analyses, we could demonstrate that THRSP is present mainly in nuclei of adipose tissue, in intramuscular fat cells and associated cells, and in cells of the portal triad of liver, whereas muscle cells did not express THRSP. Cell culture analyses revealed furthermore that THRSP is expressed in mature adipocytes rather than in early stages of adipogenesis. Collectively, our data support the putative role of THRSP as transcriptional regulator and demonstrate that an increased expression of THRSP in M. longissimus is a consequence of but not the reason for a higher number of intramuscular adipocytes in cattle with enhanced IMF deposition.
Keywords: THRSP; cattle.; intramuscular fat.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
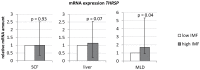




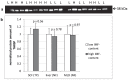


References
-
- Jump DB & Oppenheimer JH. High basal expression and 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine regulation of messenger ribonucleic acid S14 in lipogenic tissues. Endocrinology. 1985;117:2259–2266. - PubMed
-
- Tao TY & Towle HC. Coordinate regulation of rat liver genes by thyroid hormone and dietary carbohydrate. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;478:20–30. - PubMed
-
- Kinlaw WB, Ling NC, Oppenheimer JH. Identification of rat S14 protein and comparison of its regulation with that of mRNA S14 employing synthetic peptide antisera. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:19779–19783. - PubMed
-
- Kinlaw WB, Tron P, Friedmann AS. Nuclear localization and hepatic zonation of rat "spot 14" protein: immunohistochemical investigation employing anti-fusion protein antibodies. Endocrinology. 1992;131:3120–3122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

