Infantile Periocular Hemangioma
- PMID: 28540013
- PMCID: PMC5423375
- DOI: 10.4103/jovr.jovr_66_17
Infantile Periocular Hemangioma
Abstract
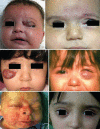
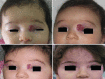
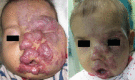
Infantile periocular hemangiomas (IPH) are common benign vascular tumors that present early in childhood. They typically show a rapid nonlinear growth pattern a few weeks after birth during a proliferative phase, then continue with an involution phase and may result in serious ocular or systemic complications. Theses tumors may present in a range of small isolated lesions to multiple, diffuse involvements. Understanding the nature of the disease, the natural course, complications, indications for intervention, and treatment modalities would be helpful for ophthalmologists, who will likely be consulted for periocular cases. In this review, we present recent opinions about the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment options for patients with IPH.
Keywords: Amblyopia; Children Eyelid Lesion; Corticosteroid Injection; Infantile Periocular Hemangioma; Systemic Propranolol.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dasgupta R, Fishman SJ. ISSVA classification. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2014;23:158–161. - PubMed
-
- Maguiness SM, Frieden IJ. Current management of infantile hemangiomas. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2010;29:106–114. - PubMed
-
- Chang LC, Haggstrom AN, Drolet BA, Baselga E, Chamlin SL, Garzon MC, et al. Growth characteristics of infantile hemangiomas: Implications for management. Pediatrics. 2008;122:360–367. - PubMed
-
- Tollefson MM, Frieden IJ. Early growth of infantile hemangiomas: What parents' photographs tell us? Pediatrics. 2012;130:e314–320. - PubMed
-
- Kilcline C, Frieden IJ. Infantile hemangiomas: How common are they? A systematic review of the medical literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 2008;25:168–173. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

