Outcome of misoprostol and oxytocin in induction of labour
- PMID: 28540049
- PMCID: PMC5433665
- DOI: 10.1177/2050312117700809
Outcome of misoprostol and oxytocin in induction of labour
Abstract
Background: Induction of labour is the process of initiating the labour by artificial means from 24 weeks of gestation. The main aim of this study is to find out the maternal and foetal outcomes after induction of labour with misoprostol and oxytocin beyond 37 weeks of gestation.
Methods: This was a hospital-based observational study carried out at Paropakar Maternity and Women's Hospital, Nepal. Misoprostol of 25 µg was inserted in posterior fornix of vagina or oxytocin infusion was started from 2.5 units on whom induction was decided. Maternal and foetal/neonatal outcomes were observed. Collected data were analysed using SPSS and MS Excel.
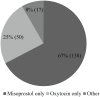
Results: General induction rate was found to be 7.2%. In this study, post-term pregnancy was found to be the most common reason for induction of labour. Analysis of onset of labour led to the finding that mean onset of labour was much rapid in oxytocin (6.6 h) than misoprostol (13.6 h). However, there is similarity in induction-delivery interval in both groups. Overall, the rate of normal delivery and caesarean section was found to be 64.9% and 33.2%, respectively. Similarly, normal delivery within 12 h was seen in 18.4% of the patients given with misoprostol and 43.5% in oxytocin group. Foetal distress was found as the most common reason for caesarean section. The overall occurrence of maternal complication was found to be similar in misoprostol and oxytocin groups, nausea/vomiting being the most common (36.7%) complication followed by fever (24.1%). Besides this, the most common neonatal complication found in overall cases was meconium stained liquor (49.2%).
Conclusion: It was found that misoprostol was used most frequently for induction of labour compared to oxytocin. The onset of labour was found to be rapid in oxytocin than misoprostol. However, the occurrence of side effects was found to be similar in both misoprostol and oxytocin groups.
Keywords: Foetal outcome; induction of labour; maternal outcome; misoprostol; neonatal outcome; oxytocin.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
Similar articles
-
EFFECTIVENESS AND SAFETY OF 2-HOURLY 20 MCG ORAL MISOPROSTOL SOLUTION COMPARED TO STANDARD INTRAVENOUS OXYTOCIN IN LABOUR INDUCTION DUE TO PRE-LABOUR RUPTURE OF MEMBRANES AT TERM: A RANDOMISED CLINICAL TRIAL AT KENYATTA NATIONAL HOSPITAL.East Afr Med J. 2014 Sep;91(9):303-10. East Afr Med J. 2014. PMID: 26866082 Clinical Trial.
-
Misoprostol in labour induction of term pregnancy: a meta-analysis.Chin Med J (Engl). 2004 Mar;117(3):449-52. Chin Med J (Engl). 2004. PMID: 15043790 Review.
-
Induction of labour in term premature rupture of membranes; oxytocin versus sublingual misoprostol; a randomised clinical trial.J Obstet Gynaecol. 2018 Feb;38(2):167-171. doi: 10.1080/01443615.2017.1329284. Epub 2017 Aug 8. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2018. PMID: 28784054 Clinical Trial.
-
Induction of labor with misoprostol for premature rupture of membranes beyond thirty-six weeks' gestation.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1998 Jul;179(1):94-9. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(98)70256-x. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1998. PMID: 9704771 Clinical Trial.
-
Induction of labour with a favourable cervix and/or pre-labour rupture of membranes.Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2003 Oct;17(5):795-809. doi: 10.1016/s1521-6934(03)00067-1. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2003. PMID: 12972015 Review.
Cited by
-
The Efficacy of Misoprostol Vaginal Inserts for Induction of Labor in Women with Very Unfavorable Cervices.J Clin Med. 2023 Jun 17;12(12):4106. doi: 10.3390/jcm12124106. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37373798 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative analysis of methods of preinduction cervical ripening and induction of labor in Poland and in Germany (Part II): maternal and neonatal outcomes.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025 Jan 27;25(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12884-024-07015-8. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025. PMID: 39871179 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of labour practices at Botshabelo District Hospital: Assessing the institutional guidelines.J Public Health Afr. 2022 Jul 26;13(2):2153. doi: 10.4081/jphia.2022.2153. eCollection 2022 Jul 26. J Public Health Afr. 2022. PMID: 36051530 Free PMC article.
-
Sublingual Misoprostol versus Oxytocin to Induce Labor in Term Premature Rupture of Membranes in Pregnant Women: A Randomized Single-Blind Controlled Trial.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Feb 13;2022:9449036. doi: 10.1155/2022/9449036. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35198639 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Is Misoprostol Vaginal Insert Safe for the Induction of Labor in High-Risk Pregnancy Obese Women?Healthcare (Basel). 2021 Apr 14;9(4):464. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9040464. Healthcare (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33919898 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO recommendations for induction of labour, http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/44531/1/9789241501156_eng.pdf
-
- Wing DA. Induction of labor. In: Queenan JT, Hobbins JC, Spong CY. (eds) Protocols for high-risk pregnancies. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Blackwell, 2010, pp. 140–147.
-
- Hofmeyr GJ, Gülmezoglu AM. Vaginal misoprostol for cervical ripening and induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003; (1): CD000941. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Preparations WECoSfP – quality assurance of pharmaceuticals: meeting a major public health challenge. 2014, http://apps.who.int/medicinedocs/documents/s21390en/s21390en.pdf
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources