Obesity and Kidney Disease: Hidden Consequences of the Epidemic
- PMID: 28540059
- PMCID: PMC5433675
- DOI: 10.1177/2054358117698669
Obesity and Kidney Disease: Hidden Consequences of the Epidemic
Abstract
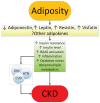
Obesity has become a worldwide epidemic, and its prevalence has been projected to grow by 40% in the next decade. This increasing prevalence has implications for the risk of diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and also for chronic kidney disease (CKD). A high body mass index is one of the strongest risk factors for new-onset CKD. In individuals affected by obesity, a compensatory hyperfiltration occurs to meet the heightened metabolic demands of the increased body weight. The increase in intraglomerular pressure can damage the kidneys and raise the risk of developing CKD in the long term. The incidence of obesity-related glomerulopathy has increased 10-fold in recent years. Obesity has also been shown to be a risk factor for nephrolithiasis, and for a number of malignancies including kidney cancer. This year the World Kidney Day promotes education on the harmful consequences of obesity and its association with kidney disease, advocating healthy lifestyle and health policy measures that make preventive behaviors an affordable option.
L’obésité est devenue une épidémie mondiale, et on projette que sa prévalence devrait croître de 40% au cours de la prochaine décennie. Cette augmentation de la prévalence a des conséquences sur le risque de diabète, de maladies cardiovasculaires et d’insuffisance rénale chronique. Un indice de masse corporelle élevé est l’un des plus importants facteurs de risque dans le développement de nouveaux cas d’insuffisance rénale. Chez les individus touchés par l’obésité, une hyperfiltration compensatoire se produit pour répondre à la demande métabolique accrue provoquée par la prise de poids. L’augmentation de la pression intraglomérulaire peut endommager les reins et augmenter le risque de développer de l’insuffisance rénale chronique à long terme. L’incidence des glomérulopathies associées à l’obésité a décuplé au cours de la dernière décennie. L’obésité a également été identifiée comme facteur de risque dans le développement de lithiases rénales et pour un certain nombre de tumeurs malignes, dont le cancer du rein. Cette année, la Journée mondiale du rein met l’accent sur l’éducation au sujet des conséquences néfastes de l’obésité et de son association avec l’insuffisance rénale, en prônant l’adoption d’un mode de vie sain et l’établissement de mesures et de politiques de santé qui font de l’adoption de comportements préventifs un choix approprié.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; kidney cancer; nephrolithiasis; obesity; prevention.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Forouzanfar MH, Alexander L, Anderson HR, et al. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;386:2287-2323. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cattaneo A, Monasta L, Stamatakis E, et al. Overweight and obesity in infants and pre-school children in the European Union: a review of existing data. Obes Rev. 2010;11:389-398. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

