Standard imaging techniques in transcatheter aortic valve replacement
- PMID: 28540072
- PMCID: PMC5422668
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2017.03.114
Standard imaging techniques in transcatheter aortic valve replacement
Abstract
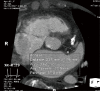
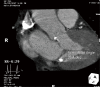
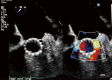
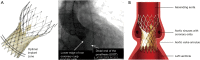
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) has become a widely accepted therapeutic option for patients with severe, symptomatic aortic stenosis at intermediate, high, or extreme risk for conventional surgery as determined through a heart team approach. Two valve prostheses are currently available and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved in the United States for TAVR: the self-expandable Medtronic CoreValve (Medtronic, Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA) and the balloon-expandable Edwards Sapien Valve (Edwards Lifesciences, Irvine CA, USA). The preoperative evaluation for TAVR includes transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) for the diagnosis of aortic stenosis. Cardiac computed tomography (CTA) has become the imaging modality of choice for annular sizing. Aortic root dimensions and coronary ostia height, and the degree of annular and left ventricular outflow tract calcification are also assessed to estimate the risk of coronary obstruction, annular rupture, and postoperative aortic regurgitation. Finally, CTA is essential to determine the adequacy of the peripheral vasculature for a transfemoral approach. Intraoperatively, fluoroscopy is mandatory for valve positioning, whereas the use of TTE or transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) varies by center. TTE is used for postoperative surveillance of valve function.
Keywords: Cardiac computed tomography (CTA); imaging; transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: A Salemi serves as clinical proctor for Edwards Lifesciences, and Medtronic, Inc. BM Worku has no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures









References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
